Fig. 3.
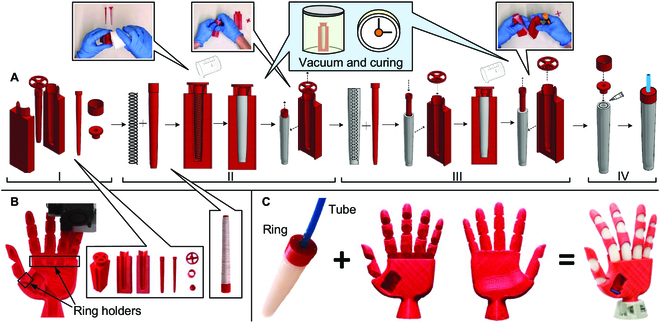
Fabrication of the soft actuators and exoskeleton. (A) Actuator’s fabrication steps using molding. In phase I, the molds and their components are 3D-printed in PLA. In phase II, the PET reinforcement is wound around the mold core, the liquid state silicone is poured into the mold, and after a period in the vacuum chamber and curing at room temperature, the unfinished actuator is removed from the mold. In phase III, the unfinished actuator is placed again in another mold to add the internal silicone layer, and after another period in the vacuum chamber and curing at room temperature, the actuator is removed from the mold. In phase IV, the actuator is glued to a rigid ring to connect the air tube and fix the actuator to the exoskeleton ring holders. (B) The exoskeleton is 3D-printed in a single processing step using FFF. (C) The 5 actuators are inserted inside each exoskeleton finger with the ring placed on the exoskeleton holder.
