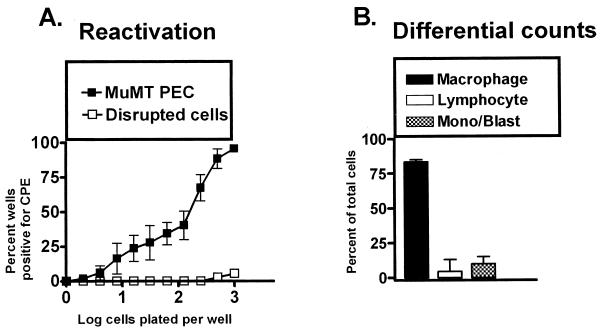
FIG. 2.
PECs from B-cell-deficient mice (MuMT[11]) harbor latent γHV68. (A) Limiting-dilution analysis to quantitate the frequency of cells that reactivate γHV68 was performed by using PECs from B-cell-deficient mice 5 to 10 weeks postinfection with γHV68. Shown are percentages of wells that scored positive for viral CPE 3 weeks after plating as a function of the number of cells plated per well. Twenty-four wells were plated per cell dilution in each experiment. Shown as open symbols are the results obtained when cells were killed by mechanical disruption prior to plating, which indicates that no preformed infectious virus was present in the samples analyzed. The data are averages of four separate experiments. Cells from 6 to 10 mice were pooled and assayed per experiment. The error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (B) Pre- and postsorting differential analysis of Wright’s-stained PECs from B-cell-deficient mice 5 to 10 weeks postinfection with γHV68. PECs were categorized by morphological criteria as macrophages, lymphocytes, or monocytes and/or lymphoblasts. Based on morphological criteria, monocytes could not always be distinguished from lymphoblasts. The data shown are averages of nine separate experiments. Cells from 6 to 10 mice were pooled and assayed per experiment. The error bars represent the standard error of the mean.