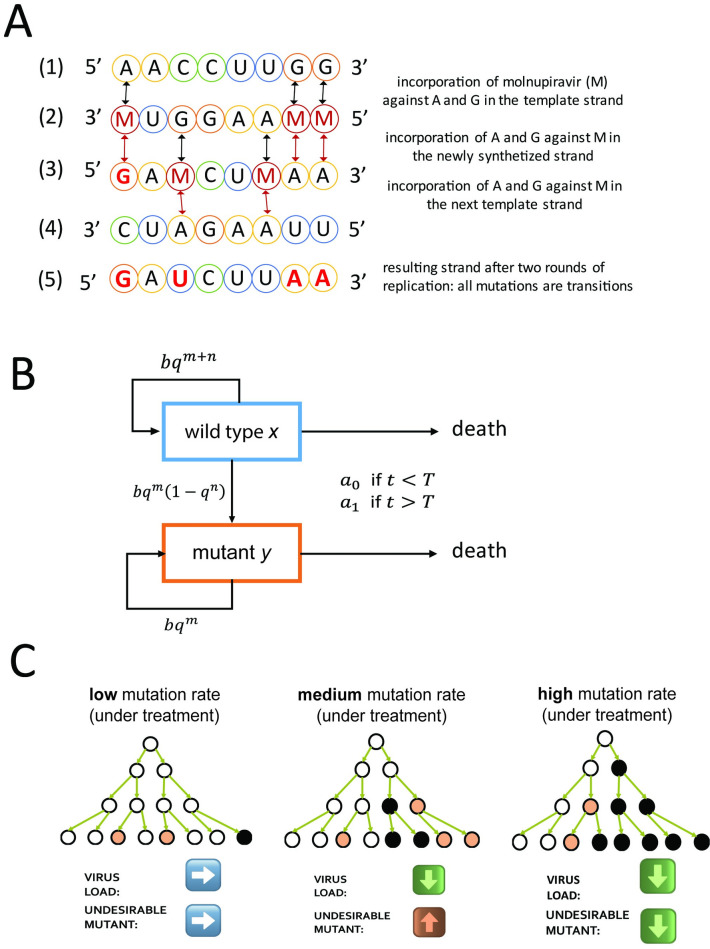
Fig 1.
(A) Mechanism of action of molnupiravir. SARS‑CoV‑2 has a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome, represented schematically in (1). Its replication proceeds in 2 steps: first, the synthesis of a negative-sense template strand (2), which is then used to synthesize a positive-sense progeny genome (3). Molnupiravir (M) is incorporated against of A or G during the synthesis of the negative-sense template strand (2). When the template strand is replicated, M can be base-paired with either G or A. Hence, all A and G in the parent genome become ambiguous and can appear as A or G in the newly synthetized positive-strand genome. C and T are not affected by molnupiravir during the synthesis of the template strand, (1) to (2), but can be substituted to M during the synthesis of the progeny genome from the template strand, (2) to (3). M can then base-pair with A or G when used as a template; see (3) to (4), which can cause A->U and U->A transitions in the final progeny genome (5). (B) Virus dynamics within an infected person. Wild type (x) and mutant (y) replicate at rate b and quality q = 1−u. The per base mutation rate, u, is increased by treatment with molnupiravir. Both wild type and mutant need to maintain m positions to remain viable. Mutating any of n positions in the wild type results in a mutant. In the beginning of the infection, the adaptive immune response is weak, and virus is cleared at a rate a0 which is less than b. After some time, T, the adaptive immunity is strong, and virus is cleared at the rate a1 which is greater than b. (C) Graphical summary of the influence of mutagenic drugs on virus mutants. White circles represent wild type, beige circles viable mutant, and black circles dead virus. When the mutation rate is low, few viable mutants and few lethal mutants are produced. Most mutations occur when the virus load is already high; hence, they have little influence on subsequent generations. For intermediate mutation rate, the total virus load declines but the amount of viable mutant increases. When the mutation rate is high, both the virus load and the amount of viable mutant decline. SARS‑CoV‑2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2.