Figure 3.
TMEM106B directly interacts with the RBD of SARS-CoV-2 spike
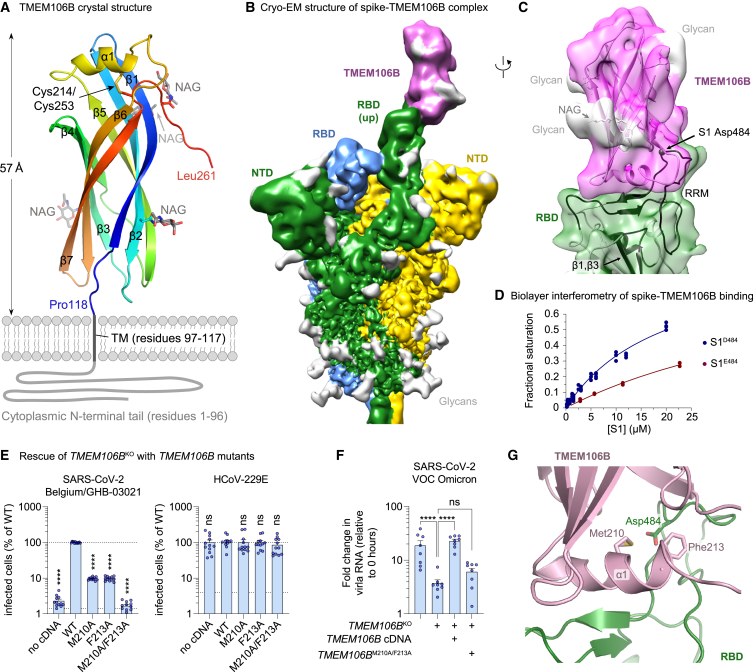
(A) The crystal structure spanning residues 118–261 of human TMEM106B, shown as cartoons, colored by the rainbow gradient from N (blue) to C (red) terminus. The remainder of the protein, comprising the transmembrane region (TM, residues 97–117) and cytoplasmic tail (residues 1–96), is schematically represented as thick gray lines. Secondary structure elements (α1, β1–β7), N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) residues, Cys214–Cys253 disulfide, the TM, and the cytoplasmic tail are indicated. NAG residues are shown as sticks with carbon atoms in gray.
(B) Cryo-EM map of the spike trimer in complex with TMEM106BLD. Protein chains are colored by protomer: subunits of the spike trimer in green, yellow, and blue and TMEM106B in magenta. The cryo-EM map features corresponding to glycans are light gray.
(C) Local reconstruction of TMEM106BLD bound to the erect RBD within the spike trimer. The cryo-EM map is shown as a semi-transparent surface, colored as in (B). The atomistic models are placed by rigid body docking and shown as cartoons. The RBD regions showing protection from HDX in the presence of excess TMEM106BLD are colored dark green.
(D) Biolayer interferometry results of S1 binding to immobilized TMEM106B. Data are represented as plots of variation of fractional saturation with S1 concentration for the S1E484 (Wuhan-Hu-1; red) versus S1D484 (Belgium/GHB-03021; blue) spike subunits. Symbols are measured values, and solid lines are computed best fits.
(E) NCI-H1975 monoclonal TMEM106BKO cells transduced with wild-type (WT) or mutant TMEM106B cDNA, infected with SARS-CoV-2 Belgium/GHB-03021/2020 or HCoV-229E. Cells were stained for dsRNA after 24 h (n = 12 wells from three experiments). Data were log-transformed and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, comparing each condition with WT TMEM106B.
(F) NCI-H1975 cells or monoclonal TMEM106BKO cells transduced with WT or mutant TMEM106B cDNA, infected with SARS-CoV-2 VOC omicron. Viral RNA in cells was measured by qPCR at 0 and 24 h post-infection (n = 8 wells from two experiments). Data were log-transformed and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(G) Close-up view of the spike-TMEM106B interface shown in (C). TMEM106B and the RBD are shown as purple and green cartoons with side chains of TMEM106B Met210 and Phe213 and spike Asp484 as sticks. Consistent with binding data (D and Figure S3F), the model predicts that the three residues project into the protein-protein interface.
(E and F) Data are mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns, not significant. See also Figures S2, S3, and S4.