Figure S2.
TMEM106B directly interacts with the RBD of SARS-CoV-2 spike, related to Figure 3
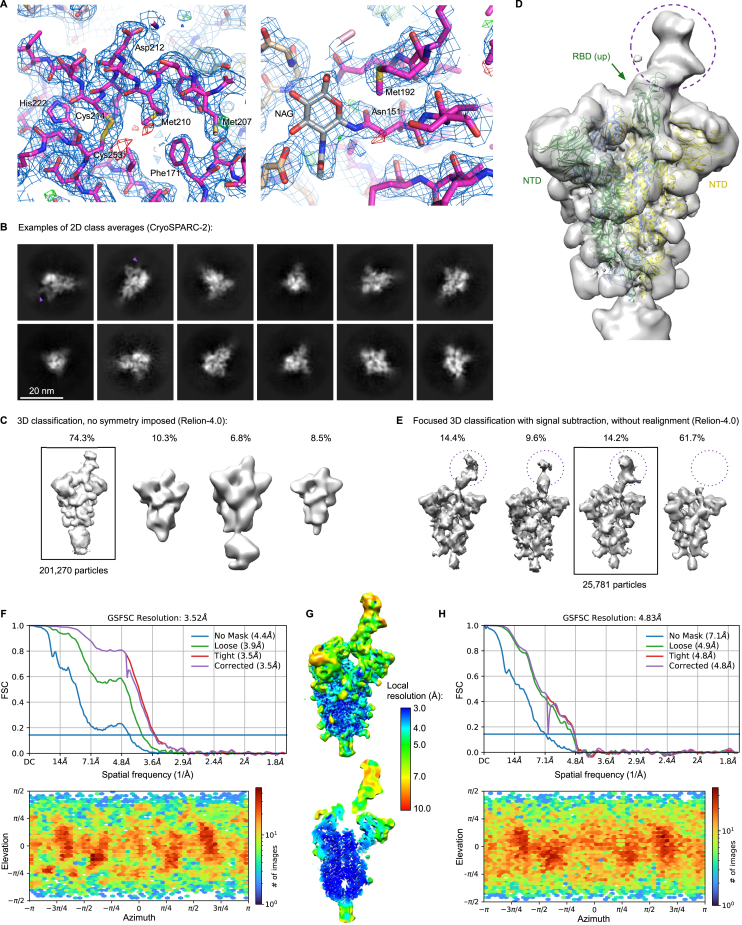
(A) TMEM106B crystal structure is shown as sticks with 2Fo-Fc electron density in blue mesh (contoured at 1 RMSD) and positive and negative Fo-Fc density in green and red mesh (contoured at 3 RMSD), respectively. The regions shown correspond to α1 helix (residues 208–216), left, and glycosylated Asn151, right. Carbon atoms of TMEM106B amino acid residues are colored magenta (chain A) or pink (molecules related by crystal symmetry). Carbon atoms of NAG residues are shown in gray. Other atoms are colored according to the standard format: oxygen, red; nitrogen, blue; and sulfur, yellow.
(B) Examples of 2D class averages of the trimeric spike ectodomain. TMEM106BLD is visible in some 2D class average (purple arrowheads).
(C) Result of the classification of the spike particles into four 3D classes. The class containing 201,270 particles selected for further processing is boxed.
(D) Unmasked 3D reconstruction using particles images selected after initial 3D classification (B). The cryo-EM map is shown as a semi-transparent surface with the feature corresponding to associated TMEM106B indicated with dotted purple circle. Fitted is an atomistic model of the spike trimer in 1RBD-up conformation (PDB: 7NTA); RBD and NTD domains are indicated.
(E) Results of focused 3D classification after signal subtraction, as detailed in the STAR Methods section. The displayed cryo-EM reconstructions were obtained after reversion to the original (non-subtracted) particles. One class selected for the final reconstruction is boxed.
(F) Resolution and particle orientation metrics for final cryo-EM reconstructions. Half-map Fourier shell correlations (FSCs) and distribution of the refined particle orientations for the result of the final global non-uniform refinement, as implemented in cryoSPARC.
(G) The final 3D reconstruction, colored by local resolution.
(H) Half-map FSCs and particle orientation for local refinement using a soft mask covering TMEM106BLD and the associated RBD.