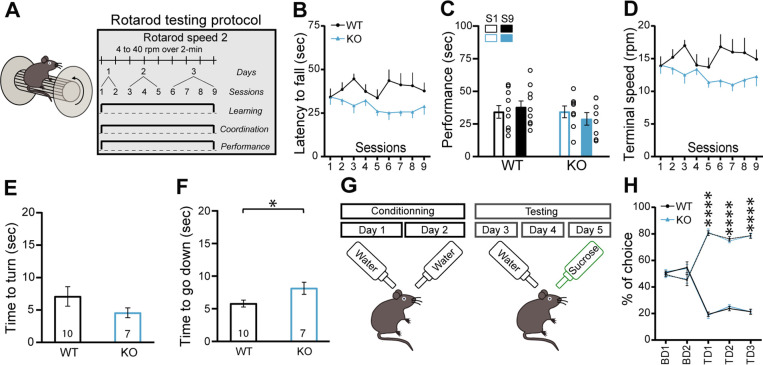
Figure 1. DAT::NrxnsKO mice exhibit impaired amphetamine-induced motor activity.
(A) Schematic representation of a mouse on a rotarod and the diagram of the rotarod testing protocol for the speed 1. (B) Performance on the accelerating rotarod during nine sessions over 3 consecutive days. Latency to fall was quantified at rotation speeds from 4 to 40 rpm over 10 min. (C) Performance of DAT::NrxnsKO and WT littermate mice on the rotarod was evaluated comparing the last session and the first session for each mouse. The results show a significant improvement in performance irrespective of genotype. (D) Quantification of the terminal speed over all the sessions shows no difference between the DAT::NrxnsKO and WT littermate mice. (E) Basal horizontal activity in a novel environment before and after a saline injection (10 mL/kg) over a total of 60 min. (F) Horizontal activity before and after a cocaine injection (20 mg/kg; 10 mL/kg) over a total of 60 min. (G) Horizontal activity before and after an amphetamine injection (5 mg/kg; 10 mL/kg) over 60 min shows reduced locomotion in the DAT::NrxnsKO compared to the control mice. For rotarod and locomotor activity experiments, 7–10 animals per group were used. For all analyses, the plots represent the mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were carried out by two-way ANOVAs followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison tests or Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. The stars in panel D represent the level of significance of the post hoc tests (*p<0.05; **p<0.01).