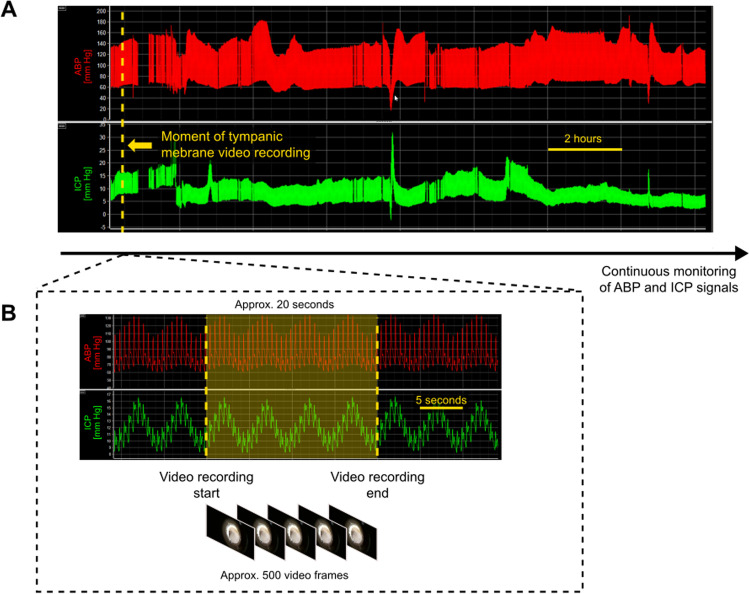
Fig. 2.
Synchronization between intracranial pressure (ICP) and arterial blood pressure (ABP) signal recordings and ‘snapshot’ video recordings of the tympanic membrane. A ICP and ABP were monitored continuously throughout the patient’s entire stay in the intensive care unit. At a time point selected by the intensivist (yellow dashed line), a video recording of the tympanic membrane was collected. B The video recording of the tympanic membrane lasted approx. 20 s (approx. 500 frames at 25 frames per second). The start and end of the recording were marked by the clinician (yellow dashed lines). The video recording was processed separately to extract spontaneous tympanic membrane displacement signal (see Fig. 3). The marked fragment of the ICP and ABP signal recordings (yellow shaded area) was used to calculate signal metrics corresponding to the time when the video was taken in order to assess if instantaneous ICP-derived parameters are reflected in tympanic membrane displacement