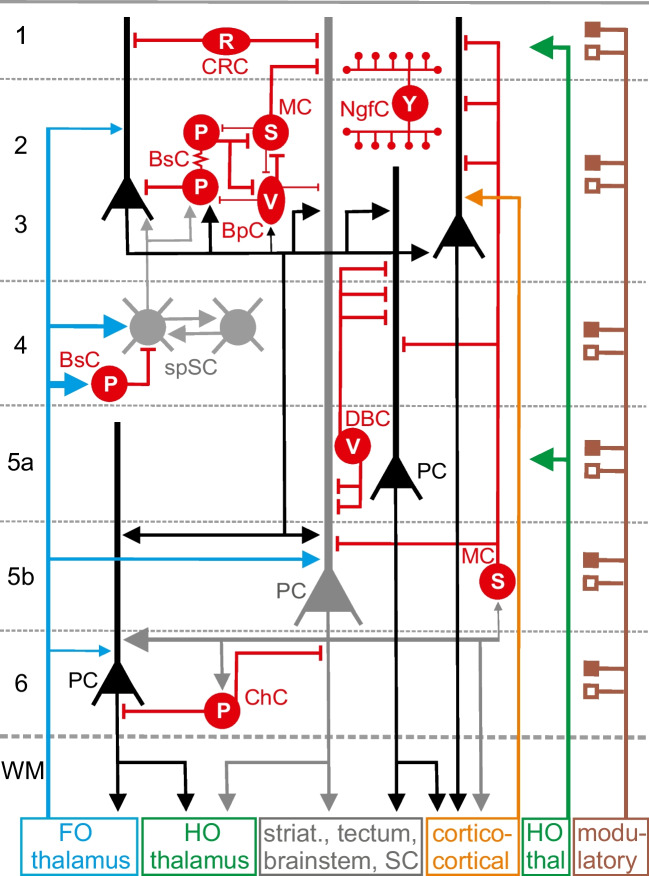
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of the neocortical microcircuitry with main afferent and efferent connections. Excitatory synaptic connections are represented by
 , inhibitory by
, inhibitory by
 ; electrical synapses by
; electrical synapses by
 , and volume transmission by
, and volume transmission by
 . Depolarizing and hyperpolarizing neuromodulatory inputs (depending on expression of postsynaptic receptors) are illustrated by
. Depolarizing and hyperpolarizing neuromodulatory inputs (depending on expression of postsynaptic receptors) are illustrated by
 and
and
 , respectively. Line thickness and arrow size indicate strength of synaptic connection, but for many connections, data are not available yet. Excitatory glutamatergic pyramidal cells (PCs) and spiny stellate cells (spSCs) are shown in black and gray. The population of inhibitory GABAergic neurons is shown in red and consists of Cajal-Retzius cells (CRC) expressing reelin (R), parvalbumin (P) expressing basket cells (BsC) and chandelier cells (ChC), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (V) expressing bipolar cells (BpC) and double-bouquet cells (DBC), Martinotti cells (MC) expressing somatostatin (S), and neurogliaform cells (NgfCs) expressing neuropeptide Y (Y). Inhibitory interneurons may express also other markers (see text). Note that GABAergic neurons not only form axo-somatic connections, but also terminate on dendritic compartments or on the axon initial segment of pyramidal neurons. NgfCs often act through volume transmission and do not form synaptic connections with postsynaptic targets. Layer-specific glutamatergic inputs from first-order (FO) and higher order (HO) thalamus are shown in blue and green, respectively; ipsi- and contralateral cortico-cortical connections in orange color. Activating and inhibiting modulatory inputs from various subcortical sources to all cortical layers are illustrated by brown color. Pyramidal neurons project in a layer-dependent manner to the striatum, tectum, brainstem, spinal cord (SC), and to ipsi- and contralateral cortex. For clarity, not all connections are shown. Examples of local micro-networks consisting of excitatory and various types of inhibitory neurons are illustrated in the upper left part
, respectively. Line thickness and arrow size indicate strength of synaptic connection, but for many connections, data are not available yet. Excitatory glutamatergic pyramidal cells (PCs) and spiny stellate cells (spSCs) are shown in black and gray. The population of inhibitory GABAergic neurons is shown in red and consists of Cajal-Retzius cells (CRC) expressing reelin (R), parvalbumin (P) expressing basket cells (BsC) and chandelier cells (ChC), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (V) expressing bipolar cells (BpC) and double-bouquet cells (DBC), Martinotti cells (MC) expressing somatostatin (S), and neurogliaform cells (NgfCs) expressing neuropeptide Y (Y). Inhibitory interneurons may express also other markers (see text). Note that GABAergic neurons not only form axo-somatic connections, but also terminate on dendritic compartments or on the axon initial segment of pyramidal neurons. NgfCs often act through volume transmission and do not form synaptic connections with postsynaptic targets. Layer-specific glutamatergic inputs from first-order (FO) and higher order (HO) thalamus are shown in blue and green, respectively; ipsi- and contralateral cortico-cortical connections in orange color. Activating and inhibiting modulatory inputs from various subcortical sources to all cortical layers are illustrated by brown color. Pyramidal neurons project in a layer-dependent manner to the striatum, tectum, brainstem, spinal cord (SC), and to ipsi- and contralateral cortex. For clarity, not all connections are shown. Examples of local micro-networks consisting of excitatory and various types of inhibitory neurons are illustrated in the upper left part