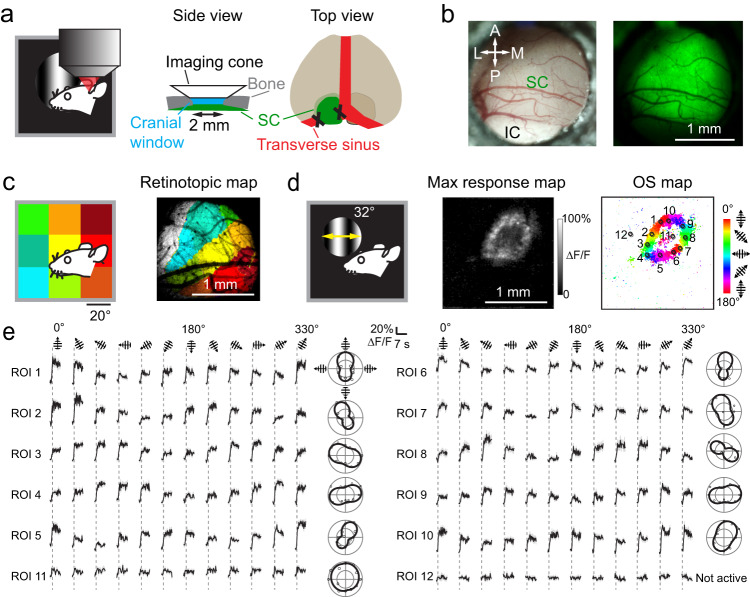
Fig. 1. In vivo calcium imaging of SC reveals orientation-selective responses at the edge of grating stimuli.
a Schematics of in vivo imaging and surgical preparation with cortex and transverse sinus overlying left SC removed and SC neurons transfected with AAV2/1.syn.GCaMP6s. b Brightfield and widefield fluorescence images of SC through a 2-mm-diameter cranial window. IC inferior colliculus. Representative results reproduced in N = 6 mice. c Example retinotopic map overlaying two-photon fluorescence image of left SC. Color denotes stimulus position. d Circular gratings spanning 32° visual field and drifting in 12 directions, map of the maximal calcium signal evoked by these gratings, and map of orientation selective pixels (pixel size: 7 µm; color-coded by preferred orientation). e Example calcium transients (ΔF/F; ten-trial average, black trace; s.e.m., gray shade) and their normalized polar plots for ROIs in (d) (ROI diameter: 56 µm). Dashed line: transition from gray screen to drifting grating.