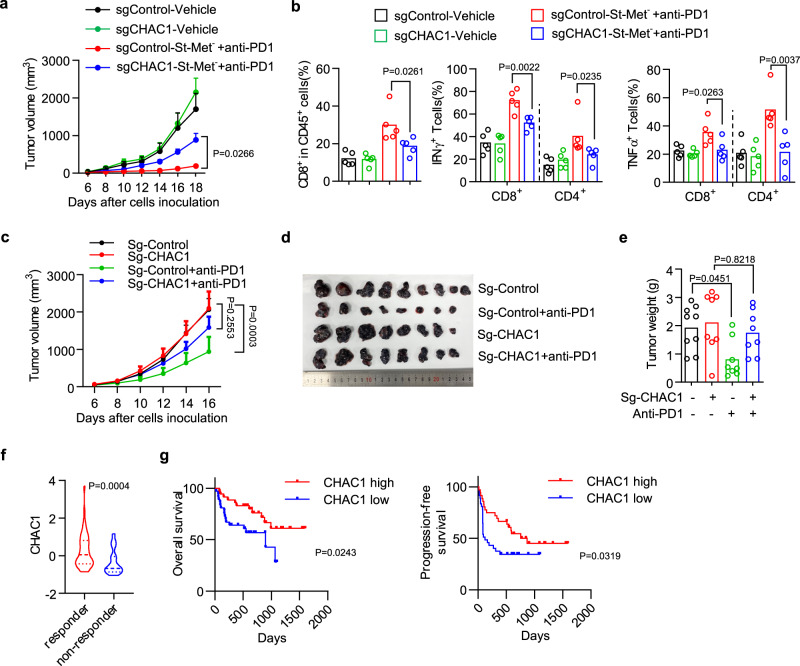
Fig. 7. CHAC1 loss in tumor cells impairs antitumor immunity.
a, b Effect of tumoral CHAC1 on combination therapy of St-Met− plus PD-1 blockade. CHAC1 wildtype (sgControl) or deficient (sgCHAC1) B16F10 tumors-bearing mice were treated by dietary methionine intermittent deprivation plus anti-PD-1 antibody. Tumor volumes were monitored over time (a). n = 7 (sg-Control-vehicle, sg-Control-St-Met−+anti-PD1, and sg-CHAC1-St-Met−+anti-PD1) or 8 (sg-CHAC1-vehicle) mice per group, data were presented as mean ± s.e.m. and P values are determined by two-way ANOVA (a). The percentages of CD8+ T cells in CD45+ cells and the percentage of cells expressing IFNγ or TNF in CD8+ and CD4+ T cells (b). n = 5 tumors per group, P values are determined by one-way ANOVA (b). c–e Effect of tumoral CHAC1 on PD-1 blockade monotherapy. CHAC1 wildtype (sg-Control) or deficient (sg-CHAC1) B16F10 tumors bearing mice (n = 8 or 9 mice per group) were treated with anti-PD-1 antibody since day 3. Tumor volumes were monitored over time (c). Data were presented as mean ± s.e.m. and P values are determined by two-way ANOVA (c). Subcutaneous tumors were surgically removed and presented (d), and their weights were measured (e). f, g Violin plot comparing tumoral CHAC1 expression between responders and non-responders of melanoma patients who received anti-PD-1 monotherapy or anti-CTLA-4 plus anti-PD-1 combination therapy49 (f ). Kaplan–Meier plots of overall survival (g, left) and progression-free survival (g, right) for these melanoma patients whose tumors demonstrate high vs. low expression of CHAC1. P values are determined by the two-sided Mann–Whitney test (f) or log-rank test (g). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.