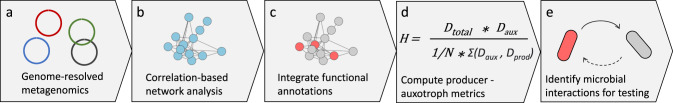
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the computational and statistical approach employed to identify microbial interactions using genome-resolved metagenomics and network analyses in this study.
First, metagenome-associated genomes are recovered and used for abundance-based correlation network analysis (a, b). Functional traits, such as vitamin biosynthesis, are inferred from the genomes and overlaid onto the network (c). The importance of nodes with a given functional annotation is estimated (d; see Methods for detailed explanation of this equation). The generated metric estimates the importance of a vitamin-producing organism for the provisioning of this vitamin to other members in the local network neighborhood. This leads to the generation of hypotheses describing potential microbial interactions (e).