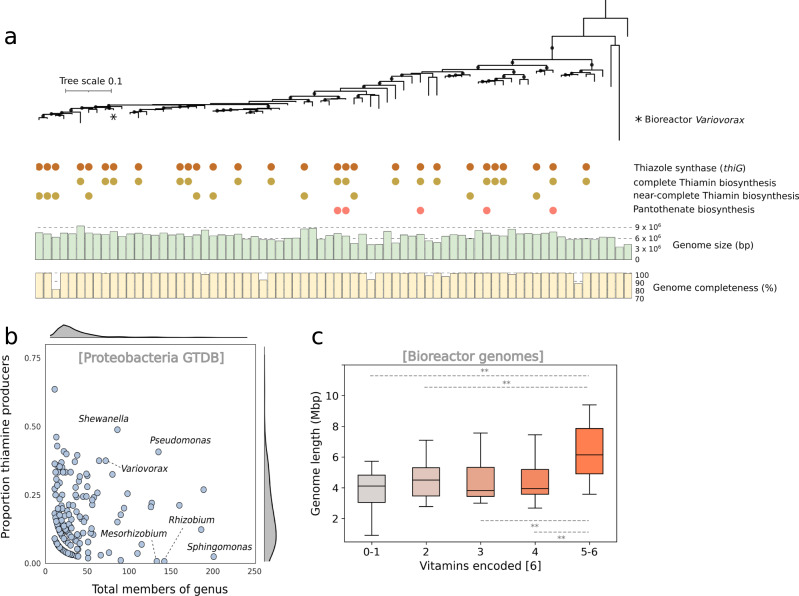
Fig. 5. Thiamine biosynthesis is common in Variovorax genomes.
a Phylogenetic tree of 16 concatenated ribosomal proteins from 70 Variovorax genomes deposited in the Genome Taxonomy Database (GTDB) together with the Variovorax isolated from our bioreactor. The encoding of a complete Vitamin B1 biosynthetic pathway is shown and was found to be encoded in 27 of the 72 GTDB Variovorax genomes. Only five of the genomes encode a complete pantothenate biosynthetic pathway. Rhodoferax saidenbachensis is shown as the outgroup. Branches supported by bootstrap values greater than 75 are shown as circles. The bioreactor Variovorax shares the greatest similarity with Variovorax sp003019815 (GCF_003019815.1). b The GTDB genomes of genera within Proteobacteria genomes in GTDB were assessed for encoding complete thiamine biosynthesis pathways. Variovorax was one of the genera with the greatest proportion of encoded thiamine biosynthesis. c The number of vitamins encoded by the 309 bioreactor-recovered genomes was assessed across genome length. Boxplot whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values within 1.5 times the interquartile range, while the bounds of the box indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles, and the center indicating the median. Genomes which encoded for the biosynthesis of 5-6 vitamins were statistically larger than those which encoded fewer (two-tailed independent samples t-test, 0.01>p > 0.001. where n0-1 = 25, n2 = 19, n3 = 31, n4 = 32 and n5-6 = 13 biologically independent microbial genomes). Vitamins encoded vs vitamin encoded #2, p-value: 0-1 and 5-6 p = 0.0014; 2 and 5-6 p = 0.0063; 3 and 5-6 p = 0.0051; 4 and 5-6 p = 0.0044.