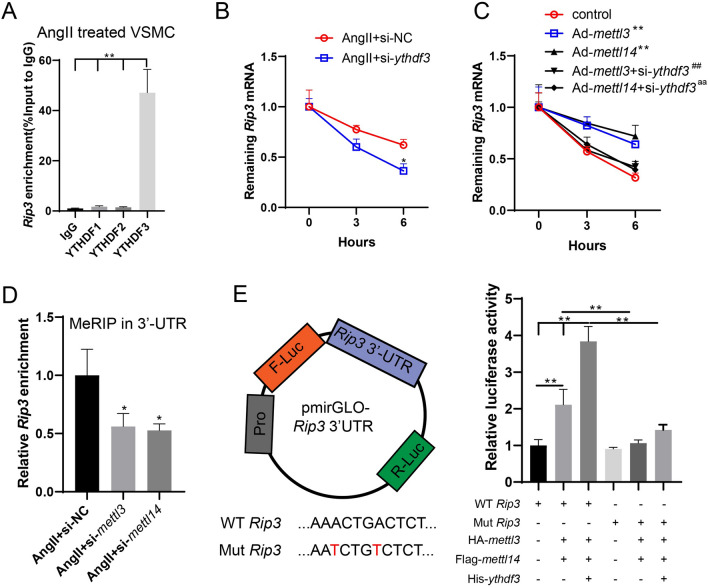
Fig. 5.
YTHDF3 promotes the stability of rip3 mRNA by recognizing the METTL3-METTL14 complex-mediated m6A binding sites. A The binding between YTHDF1/2/3 and rip3 mRNA in Ang II-treated VSMCs was confirmed by the RIP assay (n = 3, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test, **P < 0.01). B The RNA synthesis inhibitor, actinomycin D, was added to VSMCs. The expression of rip3 mRNA was detected using qRT-PCR at 0, 3, and 6 h (n = 3, two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-hoc test, *P < 0.05 vs Ang II + si-NC). C VSMCs were transfected with Ad-mettl3/mettl14 or co-transfected with si-ythdf3. The RNA synthesis inhibitor, actinomycin D, was added to VSMCs. The expression of rip3 mRNA was detected using qRT-PCR at 0, 3, and 6 h (n = 3, unpaired two-tailed t-test, **P < 0.01 vs control, ##P < 0.01 vs Ad-mettl3, aaP < 0.01 vs Ad-mettl14). D The m6A-bound rip3 enrichment in 3’UTR was detected using MeRIP (n = 3, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test, *P < 0.05 vs Ang II + si-NC). E The two predicted m6A sites were mutated and a dual luciferase plasmid vector containing wild-type (WT) and mutant (Mut) rip3 3’UTR was constructed, which was co-transfected with plasmids of HA-mettl3, Flag-mettl14, or His-ythdf3 in 293 T cells. The fluorescence activity was determined (n = 3, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test, **P < 0.01)