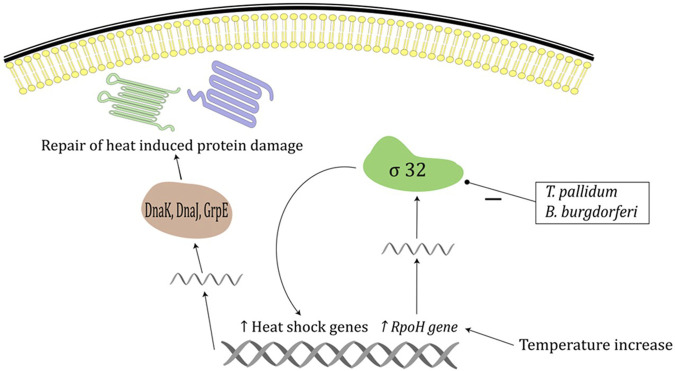
FIGURE 1.
Heat shock response in prokaryotes. Temperature increase induces increased expression of RpoH gene and increased σ 32 levels which increases expression of heat shock proteins including DnaK, DnaJ and GrpE chaperone system. Chaperone systems are responsible for repair of heat induced protein damage. Treponema pallidum and B. burgdoferi lack factor σ 32.