Fig. 1.
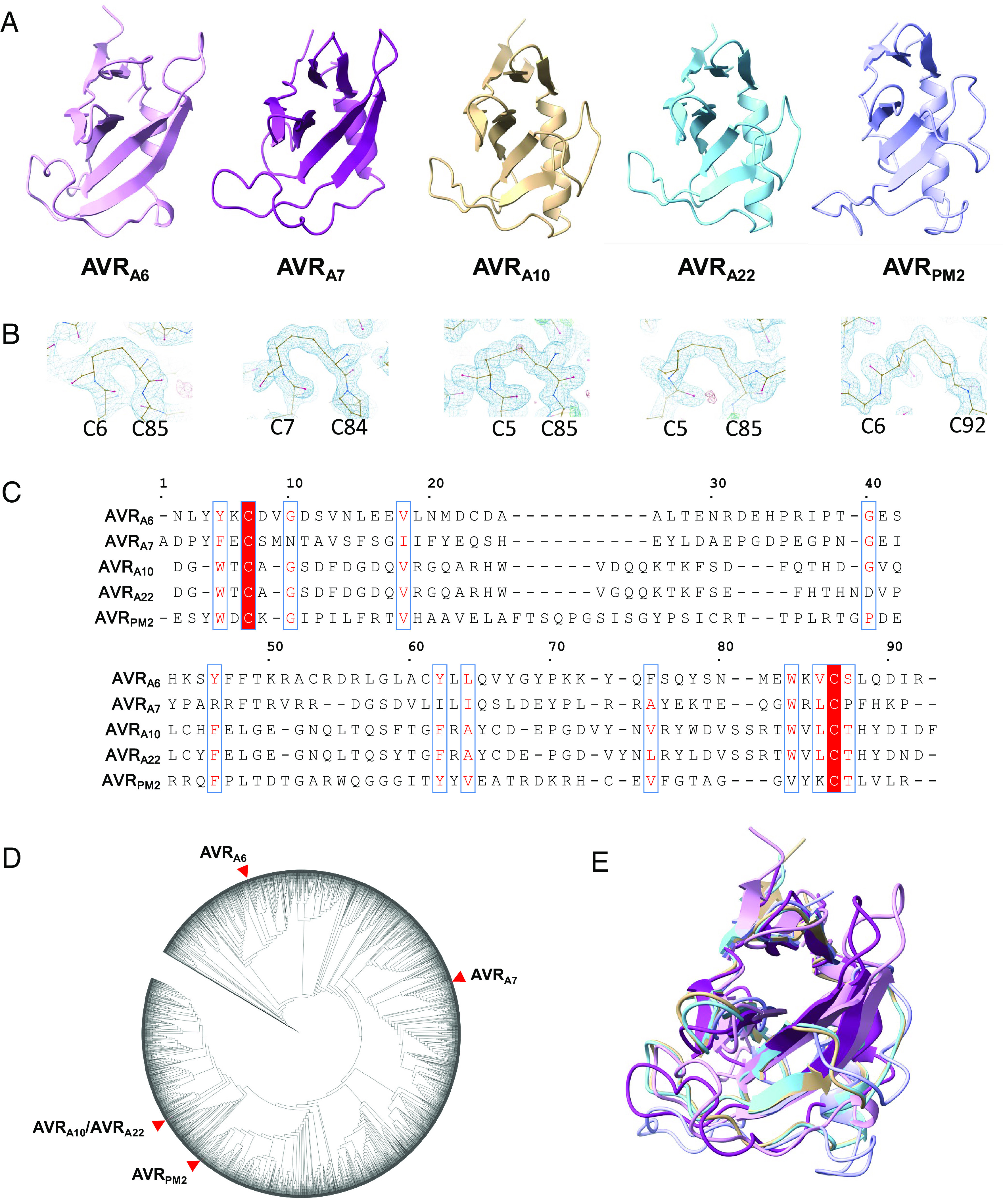
Blumeria graminis AVR effectors adopt a common structural scaffold. (A) Cartoon representation of the crystal structures of AVRA6, AVRA7, AVRA10, AVRA22, and AVRPM2. The effectors exhibit a canonical (α+β) RNase-like fold. (B) Disulfide bonds are conserved in Blumeria AVRs. AVRA6, AVRA7, AVRA10, AVRA22, and AVRPM2 form intramolecular disulfide bridges that connect the N and C termini. The disulfide bridge is indicated in the density map. (C) Amino acid sequences alignment of AVRA6, AVRA7, AVRA10, AVRA22, and AVRPM2 without signal peptides. Red background indicates amino acid similarity. The alignment was generated using ESPript 3.0 (46). (D) Maximum likelihood phylogeny including all predicted CSEPs from B. graminis f. sp. Poae, lolium, avenae, tritici 96224, hordei DH14, secalis S1459, triticale T1-20, and dactylidis. AVRA6, AVRA7, AVRA10, AVRA22, and AVRPM2 are widely separated in the phylogeny. (E) Superposition of AVRA6, AVRA7, AVRA10, AVRA22, and AVRPM2.
