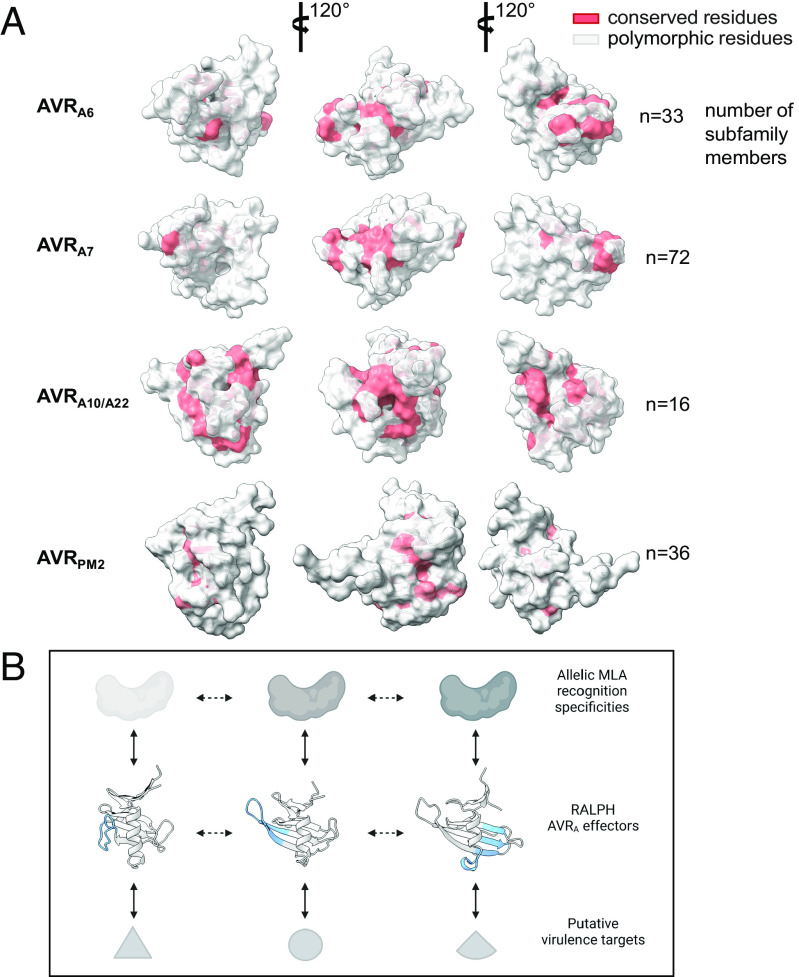
Fig. 5.
RALPH effector subfamilies harboring avirulence effectors have overlapping or distinct conserved surface arrays. (A) All CSEPs from B. graminis f sp poae, lolium, avenae, tritici 96224, hordei DH14, secalis S1459, triticale T1-20, and dactylidis were subjected to BLASTP. CSEPs that share >30% sequence identity and that are similar in size to the crystallized RALPH AVR effectors were retained for further analysis using Muscle. Red color indicates conserved (70% threshold) residues. (B) Model for MLA receptor and RALPH effector coevolution. Major local structural differences between RALPH AVRA effectors are highlighted in blue. Solid bidirectional arrows indicate selection pressure by coevolving protein pairs, dashed bidirectional arrows represent adaptive genetic changes in RALPH effectors.