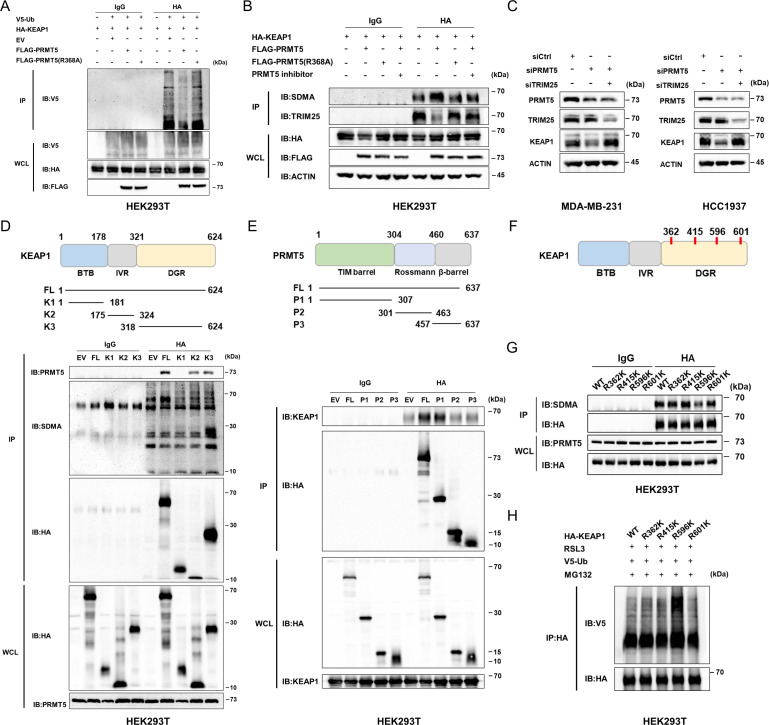
Figure 4.
PRMT5 inhibits TRIM25-mediated KEAP1 ubiquitination by inducing KEAP1R596me2. (A) Overexpression of PRMT5 suppresses the ubiquitination of KEAP1 in an arginine methyltransferase activity-dependent manner. (B) PRMT5 overexpression interfered with TRIM25 binding to KEAP1 in an arginine methyltransferase activity-dependent manner. The cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were extracted following IP and IB analysis. (C) The level of KEAP1 protein was restored by the double silencing of PRMT5 and TRIM25. (D) Representative graph showing the regions in KEAP1 that interact with PRMT5. KEAP1 179-321 aa and 322-624 aa could bind to PRMT5 while KEAP1 322-624 aa can be methylated. (E) Identification of the domain in PRMT5 involved in the interaction with KEAP1. The 1-324 aa region participates in the interaction of PRMT5 with KEAP1. (F) Representative graph showing the putative methylated residues of KEAP1. (G) R596 of KEAP1 can be methylated by PRMT5. After transfection with different plasmids, HEK293T cells were collected, and co-IP was conducted to determine methylation at the indicated site. (H) The level of ubiquitination of KEAP1-R596K was significantly lower than that of the other mutants. Average of three experiments. IB, immunoblotting; IP, immunoprecipitation; PRMT5, protein arginine methyltransferase 5; HA, anti-HA tag.