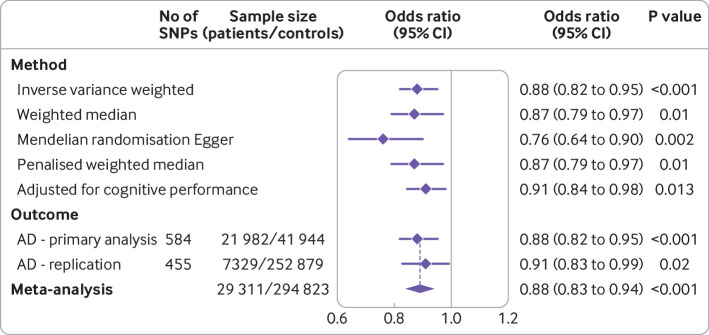
Figure 1.
Forest plot of mendelian randomisation estimates, sensitivity analyses, and replication analysis for the estimated effect of appendicular lean mass on risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Primary mendelian randomisation analysis based on the Alzheimer’s genome wide association study meta-analysis (21 982 patients and 41 944 controls). Point estimates (diamonds) are expressed as the odds ratio of Alzheimer’s disease for each standard deviation increase in appendicular lean mass (with 95% confidence intervals). Genetic variants (n=584) were used as proxies for appendicular lean mass adjusted for appendicular fat mass. Multivariable mendelian randomisation adjusting for genetically proxied cognitive performance (total 608 variants) was used to estimate the adjusted for cognitive performance effect. Also shown is replication and fixed effects meta-analysis based on genome wide association data for Alzheimer’s disease from the FinnGen consortium. AD=Alzheimer’s disease; CI=confidence interval; SNPs=single nucleotide polymorphisms