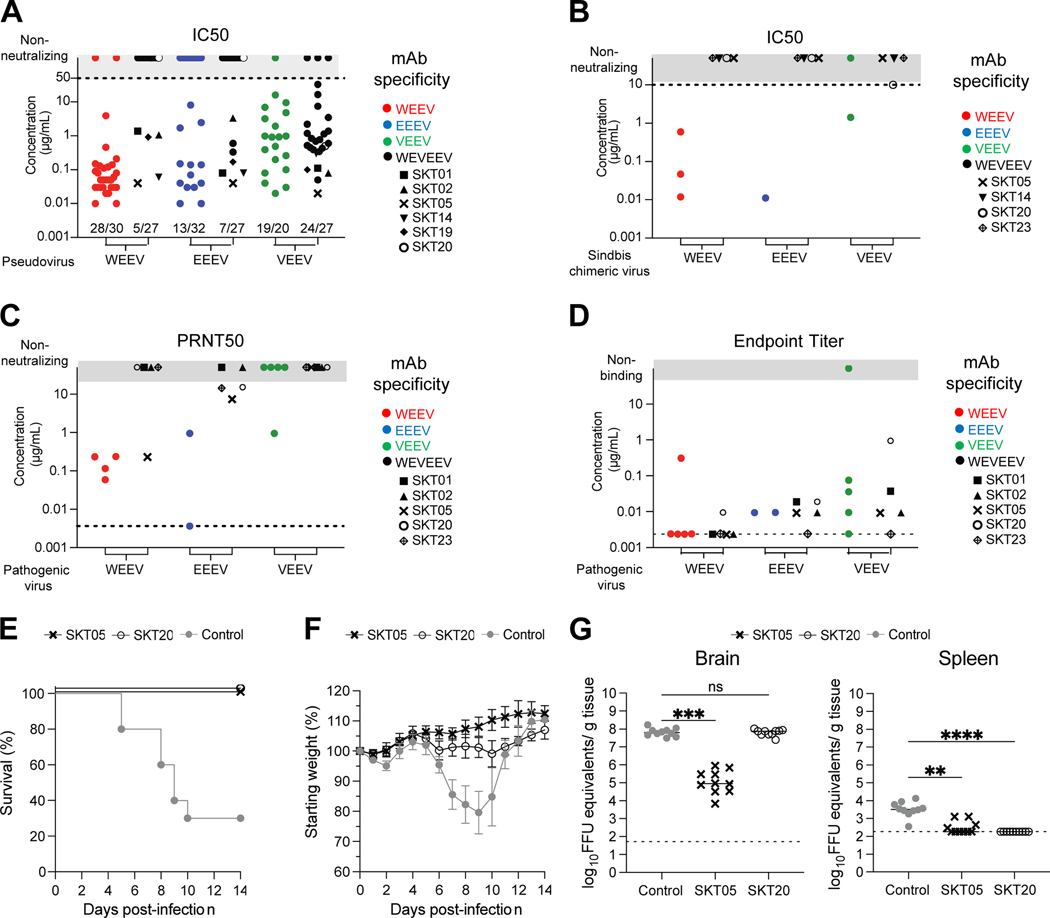
Figure 3. Vaccine-elicited ⍺-EEV mAbs bind, neutralize, and protect against encephalitic alphavirus challenge in vivo.
(A) Neutralization IC50 values for single- and triple-specific ⍺-EEV mAbs against WEEV, EEEV, and VEEV Env-pseudotyped lentiviral reporter viruses. Fractions above x-axis indicate number of neutralizing mAbs out of total tested. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments performed in triplicate. (B) IC50 values for select ⍺-EEV mAbs against SINV-chimeric viruses. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (C) PRNT50 values for select ⍺-EEV mAbs against pathogenic WEEV (Fleming strain), EEEV (FL93–939 strain), and VEEV (TrD strain). Data are shown from one experiment after determining the appropriate starting dilution. (D) ELISA endpoint binding titers for select single-specific and triple-specific ⍺-EEV mAbs against WEEV (CBA87 strain), EEEV (FL93–939 strain), and VEEV (TrD strain). Data are shown from one experiment after determining the appropriate starting dilution. In the event an endpoint titer was not identified, results are reported as half of the lowest binding titer tested and are indicated along the dotted line. (E-G) VEEV (TC-83) challenge outcome in mice (n=10/group) that received SKT05, SKT20, or a NHP ⍺-SIV mAb as a control one day prior to inoculation. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (E) Survival rate analysis and (F) change in relative weight in mice for 14 days after inoculation. (G) Viral load was determined in the brain and spleen 5 days after inoculation. Statistical significance related to viral RNA was determined by Kruskal-Wallis test (**p< 0.0021, ***p< 0.0002, ****p< 0.0001). The dotted line indicates the limit of detection for viral RNA analysis. Colors represent mAb specificity while select triple-specific mAbs are shown as unique black symbols. Only select triple-specific mAbs were assessed in B-D, all of which had unique black symbols. See also Figure S2 and Table S2.