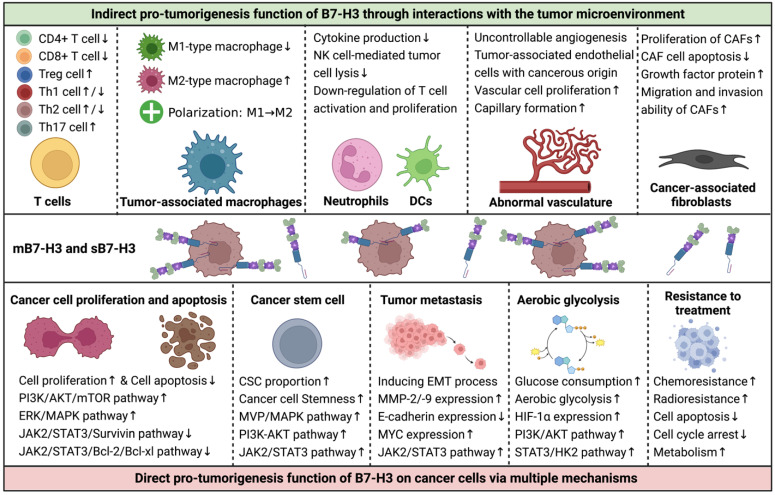
Figure 4.
Interactions of B7-H3 with the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) and Its Effects on Tumor Cells. Although the functions of B7-H3 in regulating tumor behaviors are complex, the majority of studies suggest that it plays pro-tumorigenic roles in assisting the development and progression of cancers. B7-H3 exerts its effects mainly in two ways: 1) indirectly, via communications with components of the TME, including infiltrated immune cells, aberrant vascular networks, and cancer-associated fibroblasts, and 2) directly, via multiple signaling pathways that regulate cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, stemness, invasion, migration, metabolism, and treatment responses.