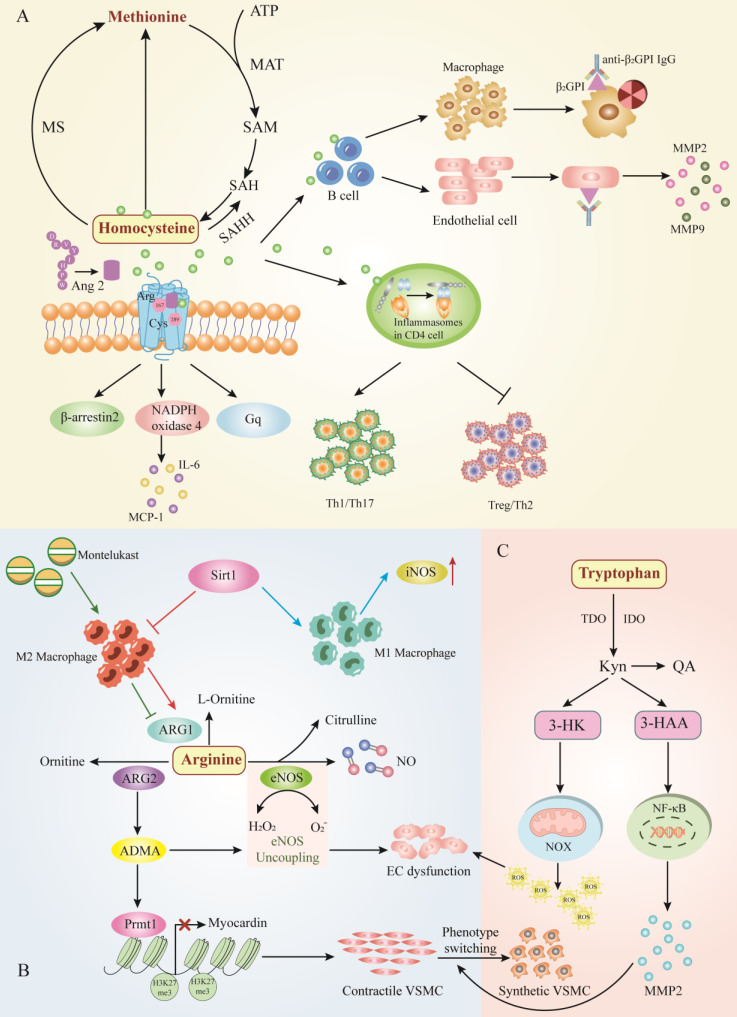
Figure 3.
The major amino acid metabolic pathway involves AAD. A.Homocysteine metabolism, B. Arginine metabolism, and C. Tryptophan metabolism. Hcy exacerbates vascular inflammation by inducing immune cells such as B cells and T cells, thereby increasing the incidence of AAD. Abbreviations: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; MAT, methionine adenosyltransferase; SAM, s-adenosylmethionine; SAH, S adenosyl L homocysteine; MS, methionine synthetase; SAHH, S adeno sylhom ocysteine hydrolase; Tfh, follicular helper T cells; Th17, T helper cell 17; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; β2GP1, β2-Glycoprotein 1; MMP2, matrix metalloproteinase 2; MMP9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; IL-6, interleukin-6; Arg, arginase; Cys, cysteine; Ang 2, angiopoietin 1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; Sirt1, Sirtuin1; ARG1, arginase 1; ARG2, arginase 2; NO, nitric oxide; ADMA, asymmetric dimethylarginine; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; EC, endothelial cell; NOX, NAD(P)H oxidase; 3-HK, 3-hydroxykynurenine; Kyn, kynurenine; QA, quinolinic acid; 3-HAA, 3-hydroxyaminobranoic acid; TDO, tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase; IDO, indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase.