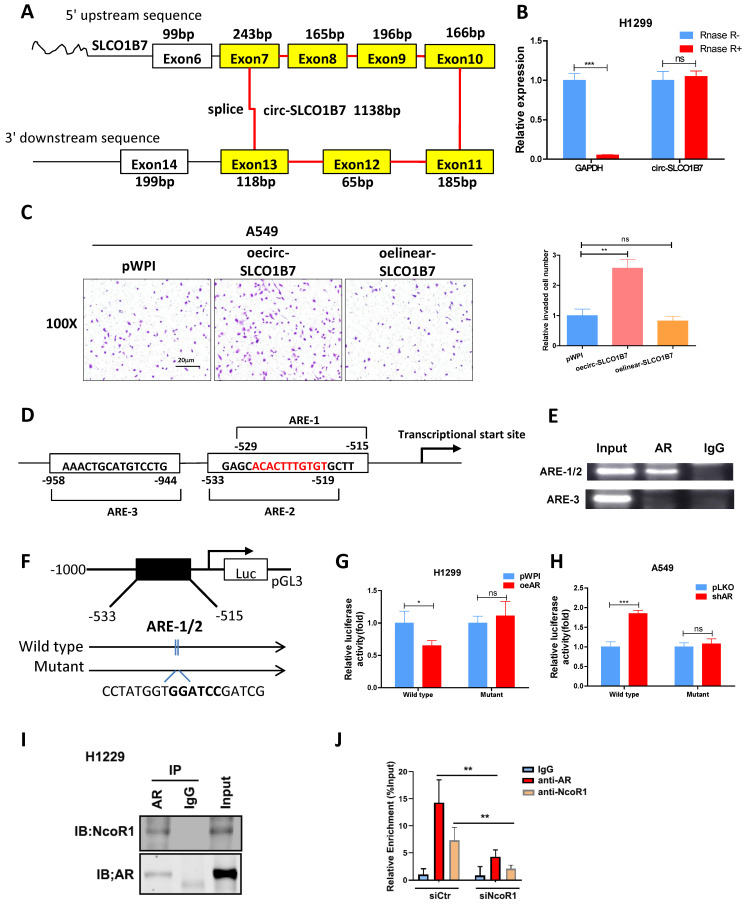
Figure 3.
Circ-SLCO1B7 enhances the invasive ability of lung cancer cell and AR transcriptionally regulates circ-SLCO1B7 expression. A. The schematic diagram illustrates the genomic location and splicing pattern of circ-SLCO1B7. B. qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of circ-SLCO1B7 and GAPDH mRNA in H1299 cells treated with or without RNase R. C. Chamber-transwell invasion assay was performed to assess the invasion capacity after the addition of circ-SLCO1B7 and linear-SLCO1B7 in A549 cells. D. Three potential androgen response elements (AREs) were predicted within the 2 kb 5'-promoter region of SLCO1B7. E. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) binding assay was conducted on H1299 cells. F. Wild-type and mutant pGL3-SLCO1B7 promoter reporter constructs were used. G-H. Luciferase activity was measured after transfection of wild-type or mutant circRNA-SLCO1B7 promoter reporter constructs in H1299 cells transfected with oeAR or pWPI (G) and in A549 cells transfected with shAR or pLKO (H). I. CoIP assay to detect the interaction of AR and NcoR1. J. NcoR1 depletion attenuated the recruitment of AR and NcoR1 to the promoter region of circ-SLCO1B7. All quantitations are presented as mean ±SD, and statistical significance was determined using the t-test, with *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 indicating significance, and "ns" representing non-significance.