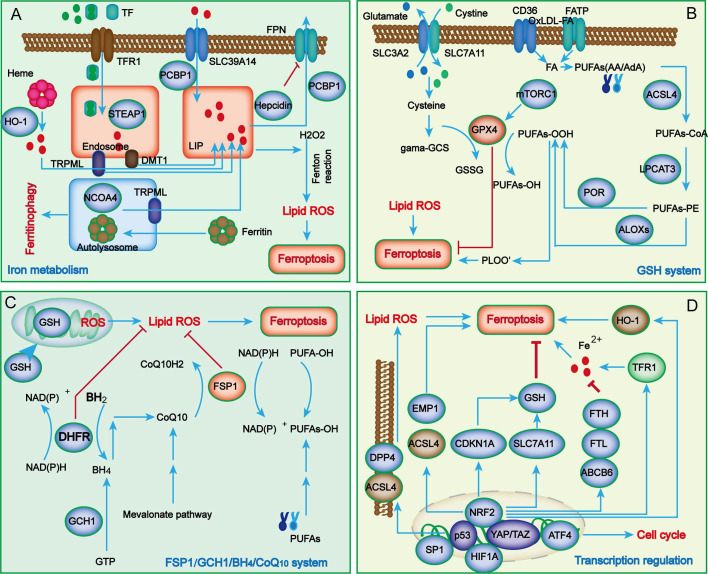
Figure 1.
The main regulatory mechanisms of ferroptosis. Iron metabolism abnormalities are the foundation of ferroptosis (A). When iron overload occurs, excess iron is stored in ferritin, and free iron participates in inducing ROS generation through the Fenton reaction. Cellular antioxidant systems eliminating lipid peroxidation of membrane phospholipids mainly function through the system Xc-/GPX4 axis (B) and other parallel metabolic pathways, including the FSP1/CoQ10/NADPH system, mitochondria DHODH/CoQH2 system, and GCH1/BH4/DHFR system (C). Recently, several key transcription regulators, such as p53, Nrf2, ATF4, SP1, HIF-1A and YAP/TAZ, have been confirmed to regulate ferroptosis (D). ABCB6, ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 6; LOXs, lipoxygenases; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; BACH1, BTB domain and CNC homolog 1; BH2, 7,8-dihydrobiopterin; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; CDKN1A, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21; CHMP5/6, chromatin modeling protein 5/6; CoQ10H2, ubiquinol; GCH1, guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase 1; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; DHODH, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; DDP4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; DMT1, divalent metal transporter1; EMP1, epithelial membrane protein 1; ESCRT-III, endosomal sorting complex required for transport III; FPN, Ferroportin; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; FTH, ferritin heavy chain; FTL, ferritin light chain; GCS, glutamylcysteine synthetase; GCH1, guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase 1; GSH, glutathione; HO-1, heme oxygenase 1; LIP, labile iron pool; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; MTX, methotrexate; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; PCBP, poly (RC)-binding proteins; POR, NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase;; STEAP3, six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 3; TXNRD1, thioredoxin reductase 1; TRPML1/2, Mucolipin TRP channel 1/2.