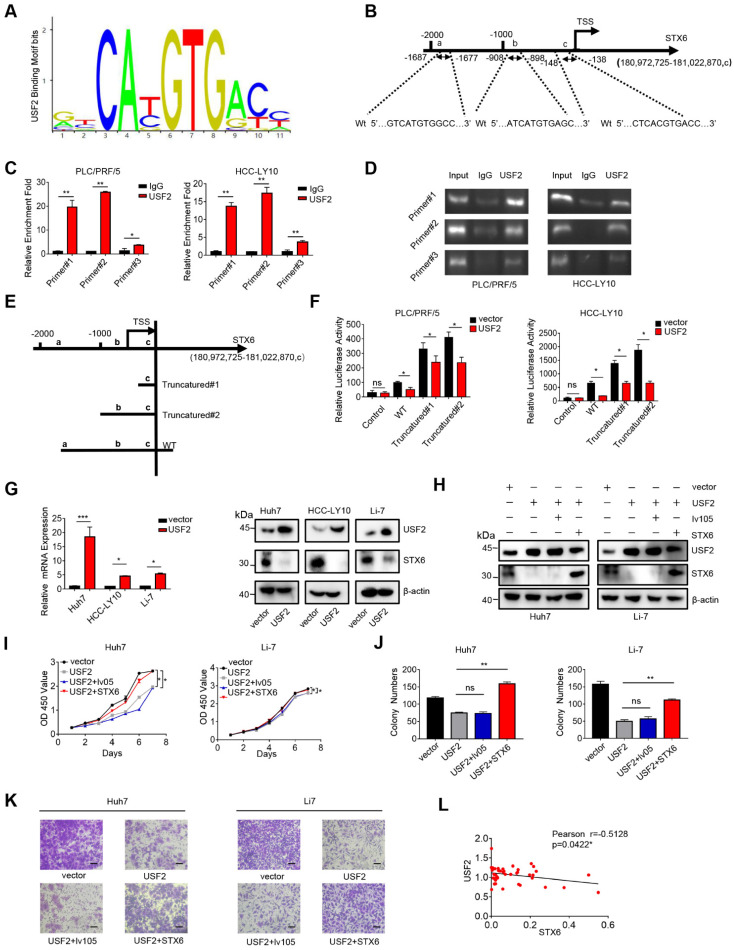
Figure 4.
USF2 binds to the STX6 promoter and inhibits STX6 expression. (A) JASPAR analysis of USF2 potential binding sites. (B) JASPAR analysis showed three potential USF2-binding sites of the promoter region of STX6. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analysis of USF2 binding to the STX6 promoter in PLC/PRF/5 and HCC-LY10 cells. (D) Agarose electrophoresis for ChIP analysis of USF2 binding to the STX6 promoter. (E) Luciferase reporter vectors containing truncation mutants of the promoter region of STX6 transfected into PLC/PRF/5 and HCC-LY10 cells. (F) Dual-luciferase reporter assays of the corresponding luciferase activities. (G) Western blot and q-PCR analysis of the protein and mRNA expression levels, respectively, of USF2 and STX6 in HCC cells after USF2 overexpression. (H) The protein levels of STX6 and USF2 in HCC cells co-overexpressing STX6 and USF2. (I and J) Cell Counting Kit-8 (I) and colony formation (J) assays of STX6 and USF2 co-overexpressing HCC cells. (K) Quantitative analysis of the Transwell assays of the invasion of HCC cells co-overexpressing STX6 and USF2. (L) STX6 mRNA level is negatively correlated with USF2 mRNA levels in 47 paired HCC tissues and adjacent matched noncancerous tissues. Data for the in vitro experiments represent the mean ± SD and are representative of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 by two-tailed Student t-test or one-way analysis of variance ANOVA. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; STX6, syntaxin-6; USF2, upstream stimulatory factor 2, Pearson correlation coefficient.