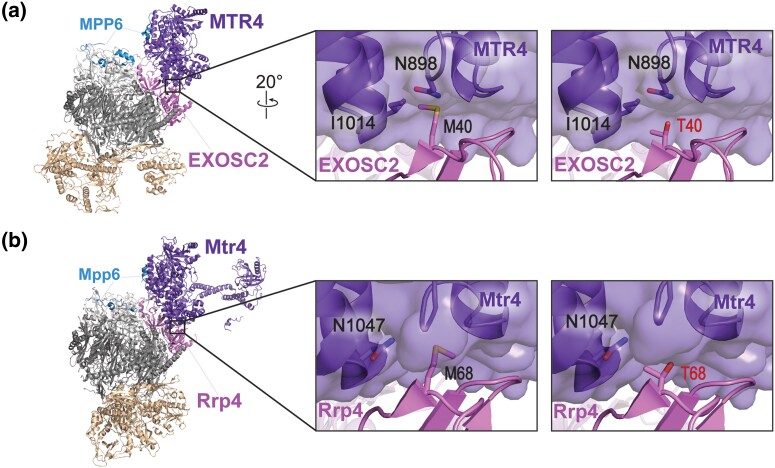
Fig. 2.
Modeling the multiple myeloma EXOSC2 M40T amino acid substitution in the human EXOSC2 cap subunit and the S. cerevisiae ortholog Rrp4. a) Structural modeling of the human EXOSC2 p.Met40Thr (M40T) amino acid substitution identified in a patient with multiple myeloma (PDB 6D6R) (Weick et al. 2018). The full structure of the human RNA exosome with the associated cofactor MTR4 (purple, labeled "MTR4") is depicted with a zoomed-in representation of the interface between EXOSC2 (pink, labeled "EXOSC2") and MTR4. Modeling of the native EXOSC2 Met40 (M40) residue (left) or the multiple myeloma-associated EXOSC2 Thr40 (T40) residue (right) is shown. The EXOSC2 Met40 residue is located in the N-terminal domain of EXOSC2, within a conserved aliphatic interface with MTR4. EXOSC2 Met40 and MTR4 associate through hydrophobic interactions, which include contacts with MTR4 Ile1014 (I1014). b) Structural modeling of the budding yeast Rrp4 Met68Thr (M68T) amino acid change, corresponding to EXOSC2 p.Met40Thr, in the budding yeast RNA exosome (PDB 6FSZ) (Schuller et al. 2018). The full structure of the budding yeast RNA exosome complex with the associated MTR4 ortholog, Mtr4 (purple, labeled "Mtr4"), is depicted on the left. A zoomed-in representation of the interface between Rrp4 (pink, labeled "Rrp4") and Mtr4 are shown, modeling the native Rrp4 Met68 (M68) residue (left) or the modeled multiple myeloma-associated substitution Rrp4 Thr68 (T68) residue (right). The Rrp4 Met68 residue is conserved between human and yeast and is located in the N-terminal domain of Rrp4. Similar to EXOSC2 Met40, Rrp4 Met68 associates with the helicase Mtr4 through primarily hydrophobic interactions, including contacts with several glycine residues in a neighboring loop of Mtr4. Parts of the human nuclear cofactor protein MPP6/MPH6 (blue, labeled "MPP6") and the budding yeast ortholog Mpp6 (blue, labeled "Mpp6") are also resolved in the structures shown in a) and b). Both MPP6/MPH6 and Mpp6 aid in stabilizing the interaction of the RNA helicase with the RNA exosome in addition to the direct interface made between EXOSC2 and MTR4 in humans or Rrp4 and Mtr4 in budding yeast (Falk et al. 2017; Wasmuth et al. 2017).