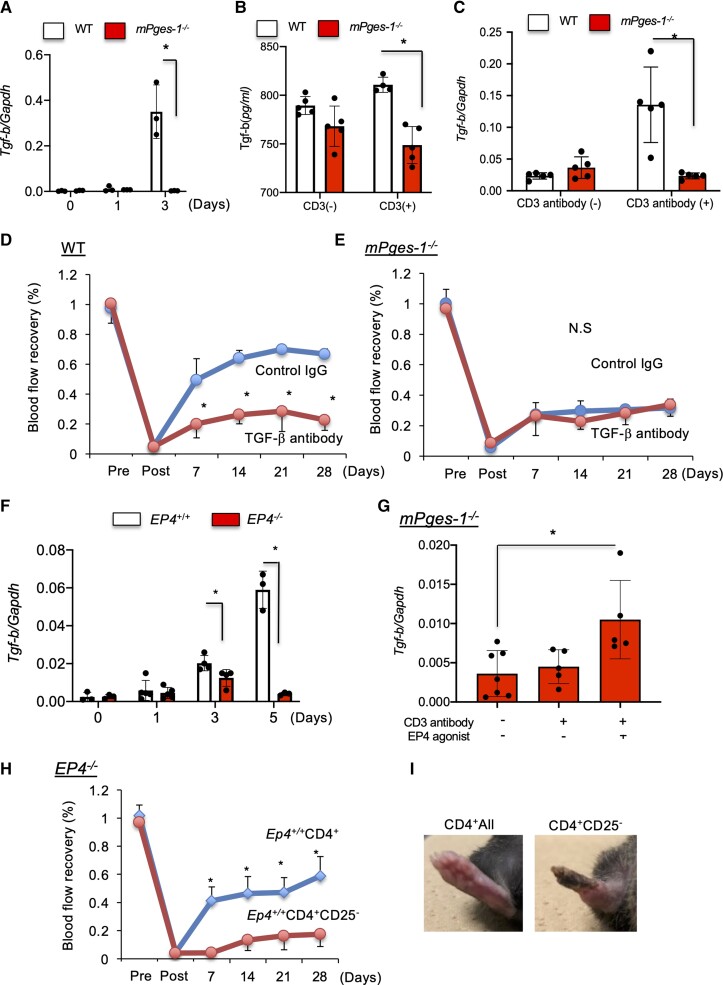
Figure 6.
The mPGES-1/EP4 axis induced recovery from ischaemia by promoting Treg TGF-β production. (A) Tgf-β mRNA expression in ischaemic muscle tissue. mPges-1−/− mice decreased mRNA expression of Foxp3 relative to WT mice. Data are means ± SD of the n = 3 mice/group. *P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA. (B) Protein level and (C) mRNA level of TGF-β in Tregs from WT and mPges-1−/− mice under CD3 antibody treatment. Expression of Ep4 was enhanced in WT Tregs. *P < 0.05, repeated-measures ANOVA. (D) In WT mice, TGF-β antibody treatment impaired blood flow recovery from ischaemia. *P < 0.05, repeated-measures ANOVA (upper panel). (E) TGF-β antibody treatment did not affect blood flow recovery from ischaemia in mPges-1−/− mice. *P < 0.05, repeated-measures ANOVA (upper panel). (F) mRNA level of Tgf-β in ischaemic muscle tissue. Ep4−/− mice decreased mRNA expression of Tgf-β compared with Ep4+/+. Data are means ± SD of the n = 3 mice/group. *P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA. (G) mRNA level of Tgf-β in Tregs from WT and mPges-1−/− mice under CD3 antibody treatment. Expression of Tgf-β in was enhanced in WT Tregs. *P < 0.05, repeated-measures ANOVA. (H) Transplantation of Ep4+/+-derived CD4+ T cells, but not CD4+CD25− T cells, into Ep4−/− recipient mice enhanced recovery from ischaemia. *P < 0.05, repeated-measures ANOVA. (I) Typical appearance of an ischaemic footpad on Day 28 in Ep4−/− transplanted with Ep4+/+-derived CD4+ T cells and CD4+CD25− T cells.