Fig. 1.
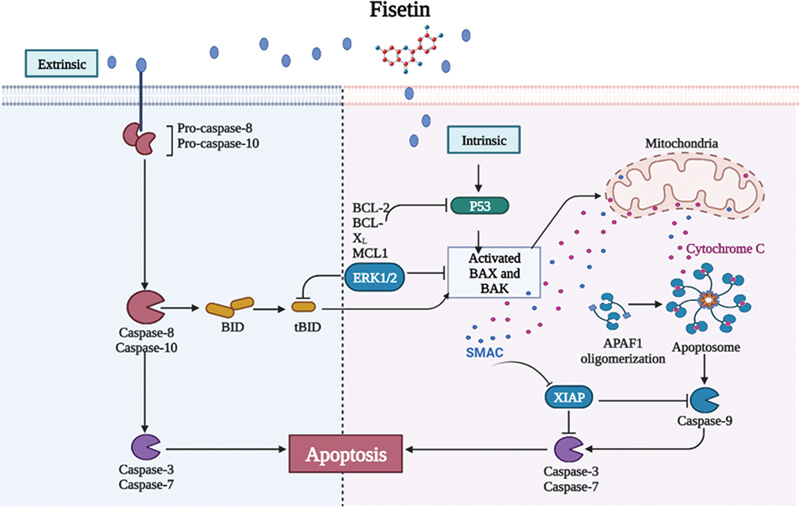
Induction of apoptosis. (1) Activation of caspase-8 by fisetin through extracellular, leading stimulating pro-caspase-8 to activate caspase-8, subsequently activating BID into tBID. Moreover, caspase-8 activates caspase-3, resulting in apoptosis. The occurrence of apoptosis can also be through intrinsic signal pathway, increasing the ratio of Bax/BAK and inhibiting Bcl-2 by fisetin through the activation of p53, which is regulated negatively by BCL-2, BCL-XL, MCL1; Meanwhile, ERK1,2 negatively regulates tBID and activates Bax/BAK, leading to the release of CytoC and over generation of ROS, which is also directly initiated by fisetin, the stimulation of AMPK and apoptosome formation under the effect of APAF, subsequently activating caspase-9 collectively, then activating caspase-3, leading to apopotosis, too. Besides both of caspase-3 and caspase-9 are inhibited by PARP, which is regulated negatively by SMAC/DIABLO. (2) Promotion of the release of Cyto C and the activation of caspase-3 and 9; (3) Upregulation of the production of ORS and activation of AMPK, leading to the production of Cyto C. Bid, AIF and the increase of the ratio of Bax to Bcl-2, causing the activation of caspase 3–9, leading to the upregulation of the production of apoptosis. “↓” indicates “to stimulate” “⊥” indicates “inhibit”; solid line represents the action directly; dotted line represents the action through several processes. Abbreviations: Bax, B cell lymphoma 2-associated X protein; MCL1, myeloid cell leukemia-1, BCL2 Family Member; Cyto C, cytochrome c; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; AIF, apoptosis-inducing factor; (Smac/DIABLO), Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase/direct inhibitor of apoptosis-binding protein with low pI; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase.
