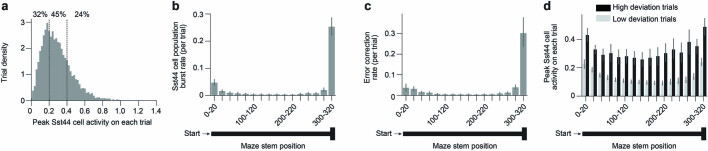
Extended Data Fig. 5. Sst44 cells activate on a subset of trials at any point along the maze, but with a strong enrichment at the T-intersection where most course corrections occur.
a, Distribution of peak Sst44 cell activity across trials. b, Sst44 cell population burst rate as a function of maze position. Sst44 cell population bursts defined as Sst44 cell population activity > 0.4 (contiguous time points that exceed this threshold are counted as one event). c, Course correction rate as a function of maze position. Course corrections defined as heading deviation > π/6 and turning accel. > 1 rad/s2 in the opposite direction, delayed by +0.3 s (to account for the average delay in the mouse’s reaction – see Methods). d, Peak Sst44 cell activity (after smoothing) for each spatial bin in each trial, splitting based on whether there was a high (> π/2) or low (< π/4) heading deviation, showing that Sst44 cell activity is strongly modulated by heading deviation at any point along the maze. Wilcoxon rank-sum test across sessions, high vs low deviation, p < 1e-6 for each spatial bin. Mean and bootstrapped 95% confidence intervals are shown. 7 mice, 27 sessions.