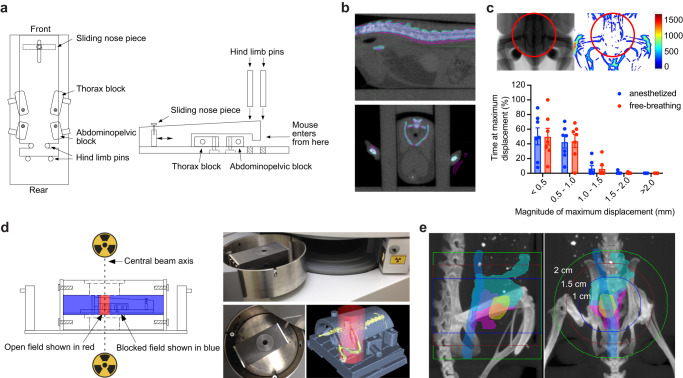
Fig. 1. Developing a stereotactic radiotherapy (RT) platform.
a Schematic of restrainer (top and side view) for delivery of stereotactic RT. b Serial imaging demonstrates negligible anatomic displacement between fractions. The pink and cyan colors indicate the bony anatomy of a mouse imaged on two separate days in the restrainer, with overlap demonstrated for the spine on sagittal view (upper panel) and pelvis on axial view (lower panel). c Intrafraction motion assessed by fluoroscopic imaging. The representative anatomic heatmap on the right shows the maximum displacement (in µm) of a free-breathing mouse during 3 min of continuous imaging. The histogram shows the percent of time that a maximum displacement occurs in the pelvic radiation field (area within the red circle). Data are plotted as mean with standard deviation (n = 7 per group). d Schematic and photographs of lead shields with interchangeable collimators (2 cm aperture shown) used to focus radiation sources located above and below the animal. Example of a focal radiation field (red cylinder) targeted to the pelvis of an immobilized mouse (skeleton in yellow). e Visualization of field size relative to pelvic organs of a male mouse. Organs were outlined on MRI and overlaid with bone windows from CT after rigid image registration. Organs depicted include bladder (yellow), prostate (pink), seminal vesicles (cyan), and colorectum (blue).