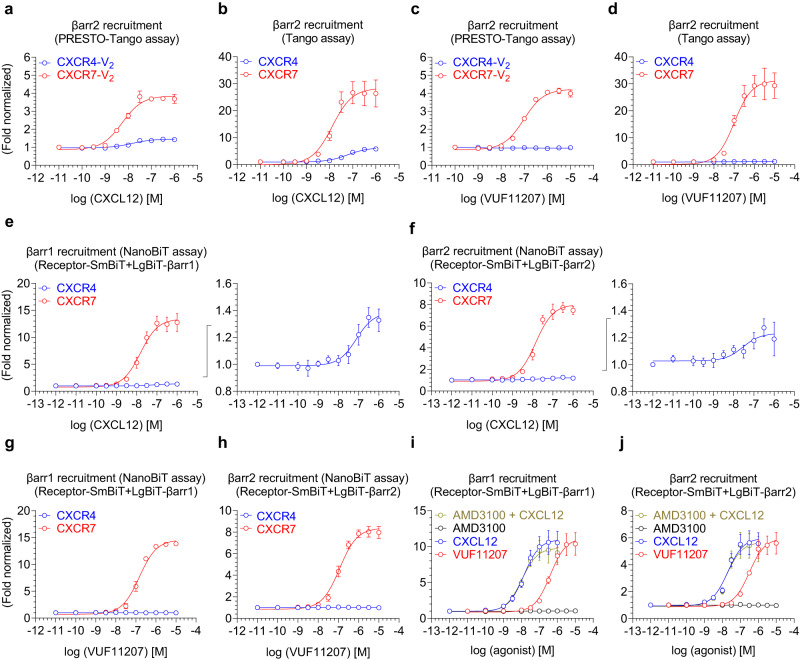
Fig. 2. β-arrestin recruitment to CXCR7.
a, b CXCL12-induced βarr2 recruitment to CXCR4 and CXCR7 in PRESTO-Tango and Tango assays, respectively (mean ± SEM; n = 3 independent experiments; normalized with the luminescence signal at minimal ligand dose treated as 1). The PRESTO-Tango assay uses a chimeric receptor construct with the carboxyl-terminus of V2R while the Tango assay uses native receptors. c, d VUF11207-induced βarr2 recruitment to CXCR4 and CXCR7 in PRESTO-Tango and Tango assays, respectively (mean ± SEM; n = 3 independent experiments; normalized with the luminescence signal at minimal ligand dose treated as 1). e, f CXCL12-induced βarr1/2 recruitment to CXCR4 and CXCR7 in NanoBiT assay (mean ± SEM; n = 4 independent experiments; normalized with luminescence signal at minimal ligand dose treated as 1). Response for CXCR4 is also shown separately in the right panels. g, h VUF11207-induced βarr1/2 recruitment to CXCR4 and CXCR7 in NanoBiT assay (mean ± SEM; n = 4 independent experiments; normalized with luminescence signal at minimal ligand dose treated as 1). i, j A side-by-side comparison of CXCL12- vs. VUF11207-induced βarr1 and 2 recruitment to CXCR7, respectively (mean ± SEM; n = 4 independent experiments; normalized with luminescence signal at minimal ligand dose treated as 1). A CXCR4-specific antagonist AMD3100 is used either alone, or as pre-treatment to CXCL12, as a negative control and to rule out the possibility of any contribution from endogenous CXCR4. Source data are provided as a source data file.