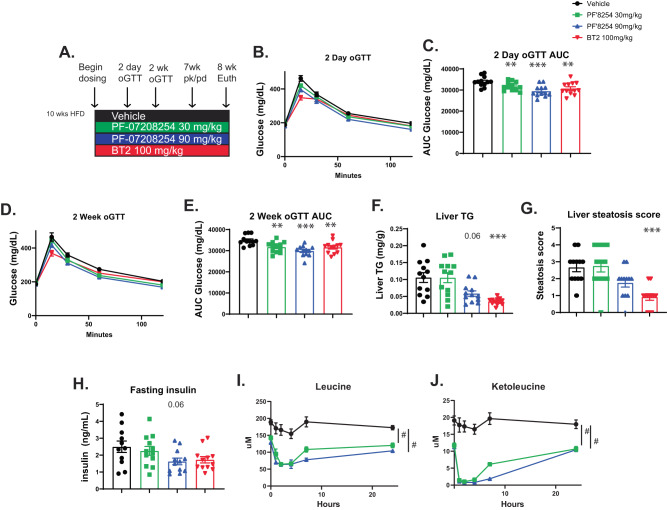
Fig. 2. PF-07208254 improves metabolism similar to BT2 and sustainably reduces BCAA and BCKA in mice.
Mice were fed HFD for 10 weeks, at which time animals were randomized into groups, and treated daily with vehicle, PF-07208254 or BT2. A Study design. B-H Oral glucose tolerance tests (oGTTs) were performed (N = 12 animals/group; a longitudinal mixed effects model with a random intercept and an AR(1) covariance structure was fit for each mouse for the glucose AUCs over the course of the study). B Day 2 oGTT. C Day 2 oGTT AUC. D Week 2 oGTT. E Week 2 oGTT AUC (**p = 0.009, ***p < 0.0001, **p = 0.009). F–H Plasma and livers were isolated 1 h post final compound dose, and steatosis was evaluated by histology (N = 12 animals/group). F Hepatic triglycerides (statistics performed with pairwise Wilcoxon test, ***p = 0.003). G Hepatic steatosis was graded by a veterinary pathologist on a scale of 0-4. (Statistics was performed using a Kruskal Wallis test followed by a Dunn test to compare within groups, ***p = 0.001). H Plasma insulin levels (N = 11–12 animals/group; statistics performed by one-way ANOVA). I, J A PK/PD assessment was performed after 7 weeks of treatment in which mice are dosed with compound, and timed bleeds were performed to measure drug levels, BCAA, and BCKA levels (N = 6–12 animals/group; statistics performed with one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD test). I Leucine (#p < 0.0001), J Ketoleucine (#p < 0.0001). Data represent the mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.