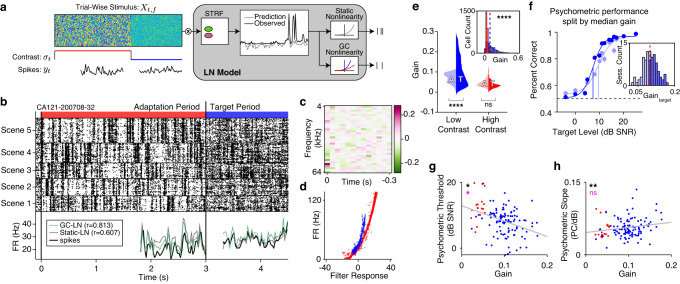
Fig. 6. Cortical gain predicts session-to-session variability in behavioral performance.
a Schematic of the LN model fit to neuronal responses during the behavioral task. b Spike raster of a representative unit recorded during the behavioral task, sorted by the background scene presented in each trial. Below is the average spike rate (black trace) overlaid with the LN model fit with a static (gray) or gain-controlled nonlinearity (green). c STRF for the representative cell. d The fitted nonlinearities in low and high contrast periods of the trials. e Gain distributions across all recorded neurons as a function of contrast and trial period (A adaptation, T target). Gain was significantly larger in the target period during low contrast (two-way ANOVA: p = 3.77e−9) but not in high contrast (p = 0.18) Inset: the average gain in low and high contrast for all cells, dashed lines indicate the median of each distribution. Gain was higher in low contrast (two-way ranksum: p = 1.60e−91. f Psychometric curves split by the median gain (n = 107 sessions). Light colored dots indicate performance across sessions with low gain, dark colored dots indicate performance on sessions with high gain. Error bars indicate ±SEM. Inset: the distribution of gain values on the same sessions. The dashed red line indicates the median used to split the data. g Relationship between session-to-session changes in gain and behavioral thresholds (n = 124 sessions). Each dot is a session, with the color indicating the contrast in which targets were presented. The gray line is the linear best fit. Black asterisks indicate whether gain is a significant predictor of the psychometric threshold, while magenta asterisks indicate whether contrast was a significant predictor of behavioral thresholds (Supplementary Table 1). h Same formatting as g, but plotting the relationship between gain and psychometric slope (n = 124 sessions). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.