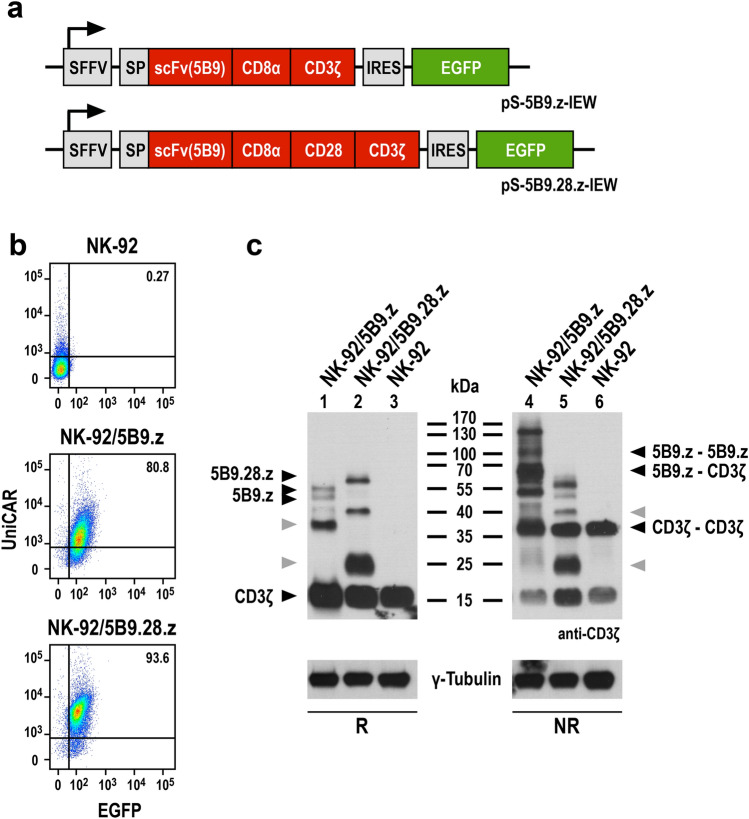
Fig. 1.
Generation of UniCAR-NK-92 cells. a Lentiviral transfer plasmids encoding first- and second-generation UniCARs under the control of the Spleen Focus Forming Virus promoter (SFFV). In pS-5B9.z-IEW the chimeric antigen receptor consists of an immunoglobulin heavy-chain signal peptide (SP), the 5B9 scFv antibody fragment specific for the E5B9 epitope, a CD8α hinge region (CD8α), and transmembrane and intracellular domains of CD3ζ (first-generation UniCAR 5B9.z). The pS-5B9.28.z-IEW vector encodes a similar CAR, but with transmembrane and intracellular domains of the costimulatory CD28 molecule and the intracellular domain of CD3ζ (second-generation UniCAR 5B9.28.z). The CAR sequences are followed by an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) and enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) cDNA. b EGFP expression of sorted NK-92/5B9.z and NK-92/5B9.28.z cells was determined by direct flow cytometry. UniCAR surface expression was detected using His-Tag-conjugated Protein L and His-Tag-specific secondary antibody. Parental NK-92 cells served as control. c Lysates of UniCAR-engineered and parental NK-92 cells were subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing (R, left panel) or non-reducing conditions (NR, right panel) and subsequent immunoblotting with CD3ζ-specific antibody. The positions of CAR monomers, CAR 5B9.z homodimers, heterodimers of CAR 5B9.z with endogenous CD3ζ, and CD3ζ homodimers are indicated by black arrowheads. Bands likely representing products of proteolytic degradation are indicated by gray arrowheads. γ-Tubulin served as loading control