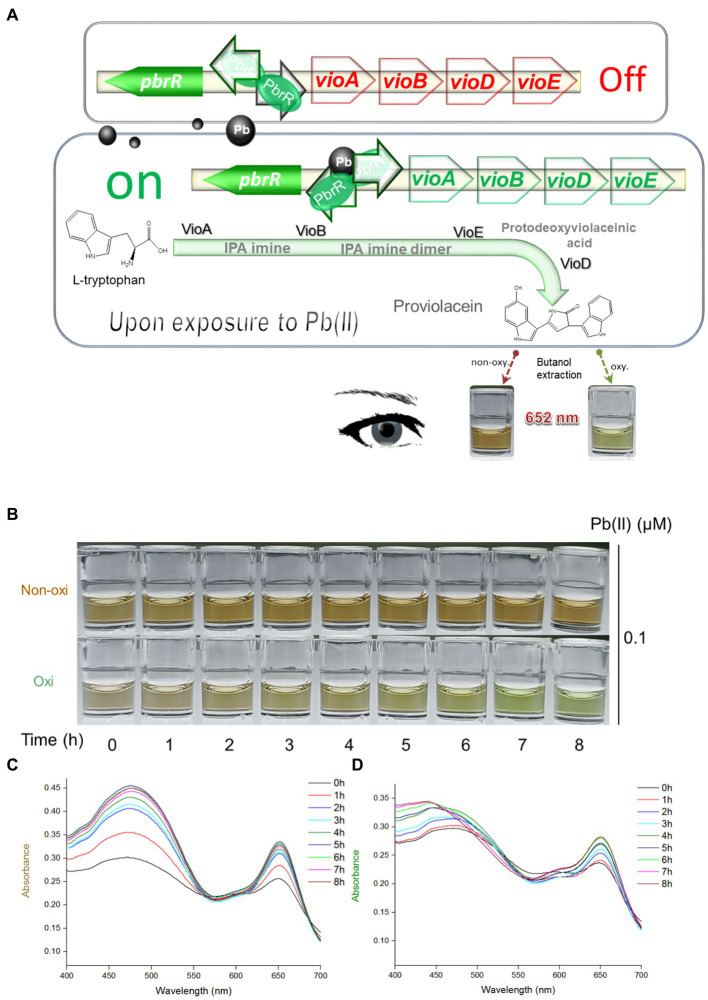
Figure 1.
Pb(II) triggers the biosynthesis of proviolacein, which can be converted into two colored substances under non-oxidizing and oxidizing conditions. (A) Design of PV-based whole-cell biosensor toward Pb(II). The PV biosynthetic module is artificially synthesized and genetically fused downstream of the Pb(II) sensory module. A tetracistronic unit is transcribed upon exposure to intracellular bioavailable Pb(II). PV biosynthesis is based on the branched violacein biosynthetic pathway catalyzed by VioA, VioB, VioE, and VioD. After n-butanol extraction accompanied by oxidation and non-oxidation treatments, PV in the organic phase was converted into two colored substances. PbrR, Pb(II) responsive metalloregulator; IPA, indole-3-pyruvate acid imine; oxy, oxidizing condition; non-oxy, non-oxidizing condition. (B) After non-oxidation and oxidation treatment, the n-butanol phase containing PV was placed at 25°C for 8 h. Representative photos from three independent experiments are shown. Visible absorption spectra of PV derivatives after non-oxidation (C) and oxidation (D) treatment were scanned at 1-h intervals. The wavelength range is from 400 to 700 nm in 1 nm intervals. Representative results from three independent assays are shown.