Figure 1.
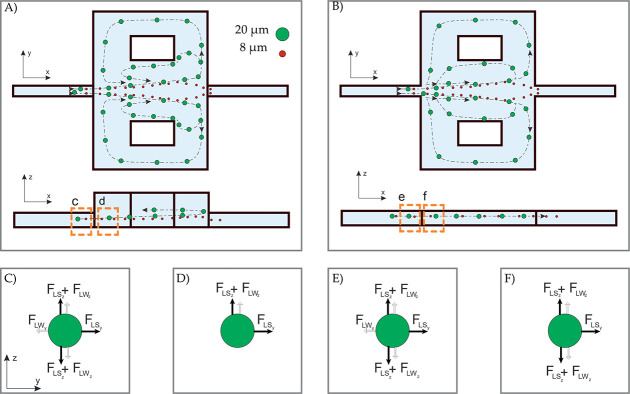
Fundamental of the vortex separation mechanism in (A) the ECR and (B) the CHC for the same Re. It can be observed that the ECR reaches the whole-cell vortex at a lower flow rate compared to CHC. The predominant forces acting on the particle are depicted before and after entering the reservoir. (C) The balance of wall and shear-induced lift forces across the y and z-axis. (D) The remaining forces cause imbalance and alter the velocity direction. (E) The balance of active forces in CHC. (F) The imbalance of dynamic forces leads to changes in velocity direction.