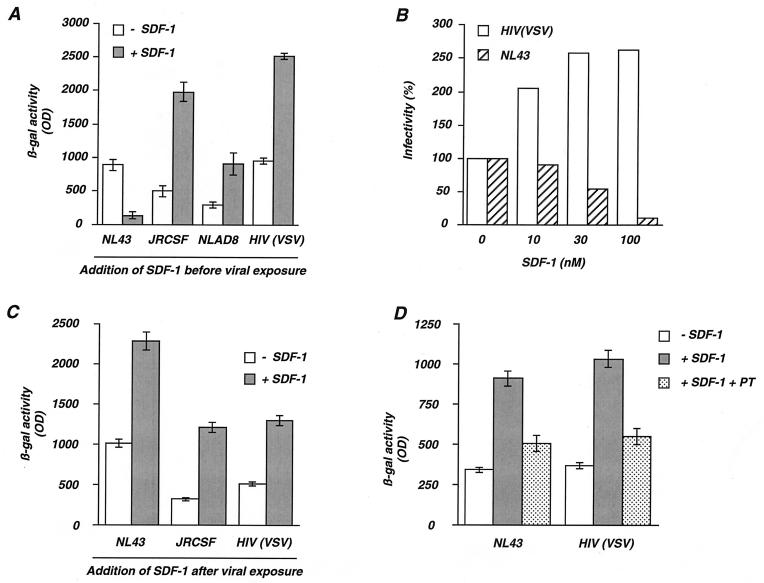
FIG. 1.
Opposite effects of SDF-1 on HIV replication. (A). Effect of SDF-1 added before virus exposure. P4C5 indicator cells (HeLa CD4+ CXCR4+ CCR5+ LTR-lacZ+) were preincubated for 20 min in the absence (− SDF-1) or in the presence (+ SDF-1) of SDF-1 (300 nM) and exposed to either NL43 (X4 strain), JRCSF and NLAD8 (R5 strains), or HIV(VSV), a defective HIV-1 with the env gene deleted and pseudotyped with the VSV-G envelope. Virus doses were 5 ng of p24 for NL43, JRCSF, or NLAD8 and 1 ng of p24 for HIV(VSV), which is more infectious (33). After 24 h, the cells were lysed and β-gal activity was measured in the cell extracts. The values are the means ± standard deviations of triplicates. (B) Dose-response analysis of the effect of SDF-1. P4C5 cells were preincubated with or without SDF-1 and exposed to NL43 or to HIV(VSV). After 24 h, the cells were lysed and β-gal activity was measured. For each indicated concentration of SDF-1, the values are expressed as percent infectivity, with 100% corresponding to the β-gal activity induced by each virus in the absence of SDF-1. (C) Effect of SDF-1 added after virus exposure. P4C5 cells were exposed for 2 h to NL43, JRCSF, or HIV(VSV), and unbound virus was removed. After 16 h, the cells were incubated with SDF-1 (100 nM), and β-gal activity was measured 9 h later. The values are means ± standard deviations of triplicates. (D) The stimulatory effect of SDF-1 is inhibited by pertussis toxin. P4 cells were exposed for 2 h to NL43 or HIV(VSV), and unbound virus was removed. After 16 h, the cells were incubated for 1 h with or without pertussis toxin (PT) (5 μg/ml). SDF-1 (200 nM) was then added as indicated, and β-gal activity was measured 9 h later. The values are means ± standard deviations of triplicates. Similar results were observed with P4C5 cells or when smaller amounts of pertussis toxin (50 ng/ml) were used (not shown). The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. OD, optical density.