Figure 2.
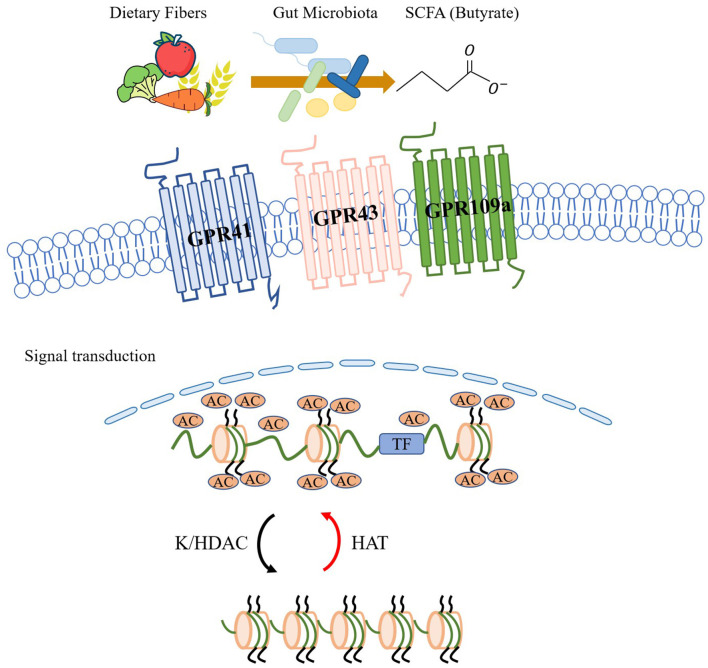
The gut microbiome has the ability to utilize dietary fiber to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like acetate. These SCFAs can activate G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) such as GPR43, GPR41, and GPR109a, and initiate signal transduction. SCFAs also exert significant inhibitory effects on lysine/histone deacetylase (K/HDAC) activity. Through their HDAC inhibitory effects and histone acetyltransferase (HAT) promoting effects, SCFAs increase histone acetylation, which in turn promotes histone translational modifications and regulates systemic immune responses.