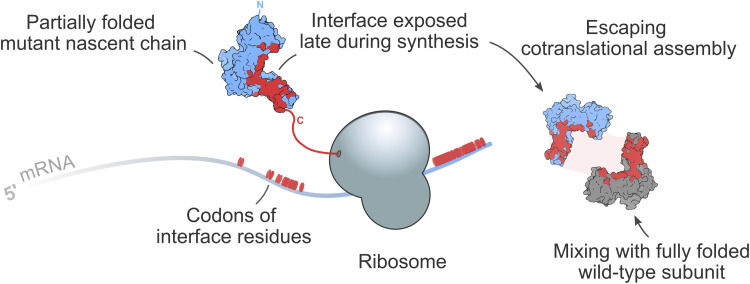
Fig. 6. Mechanistic interpretation of C-terminally shifted interfaces in homodimers with DN mutations.
Schematic representation of a structural trend underlying pathogenic DN effects. A mutant subunit is more likely to assemble posttranslationally when it exposes its interface residues late in the translation process, which can increase the level of mixing with the wild-type subunit.