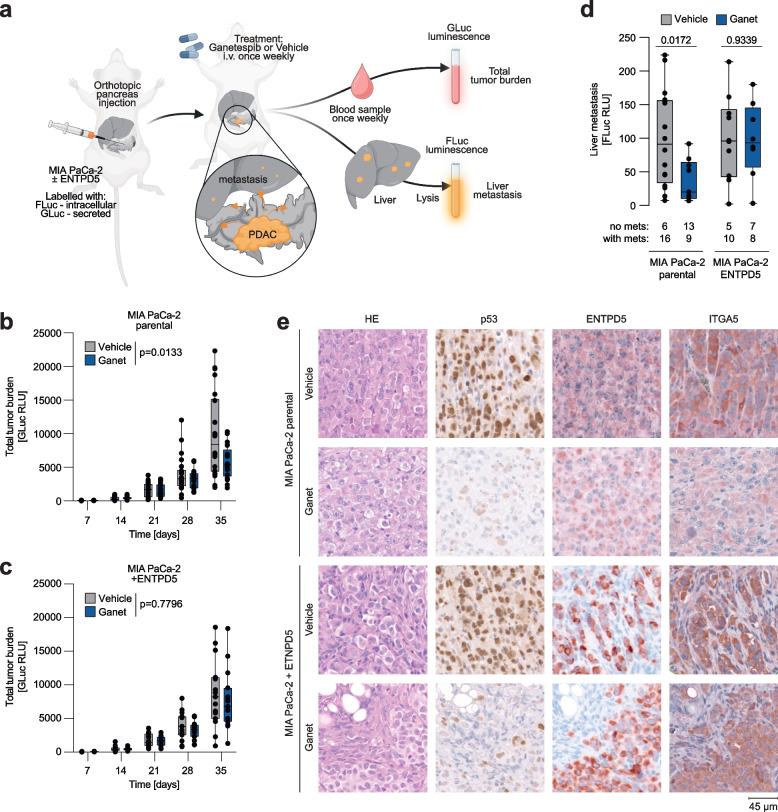
Fig. 7.
Targeting mutp53-ENTPD5 signaling inhibits ITGA5 expression, tumor growth, and metastasis in a preclinical PDAC model. a PDAC model: parental MIA PaCa-2 and MIA PaCa-2 pIND-ENTPD5 cells (with tet-inducible expression of ENTPD5) were ex vivo labeled with a tandem GLuc-FLuc construct and orthotopically injected into the pancreas of immunodeficient mice. Mice were treated with either Ganetespib (Ganet) or vehicle. All mice received doxycycline. Total tumor growth was measured by blood levels of GLuc. Liver metastasis was quantified by FLuc measurement of liver lysates. Image created with BioRender.com. b-c Total tumor growth in mice transplanted with (b) parental (n = 22 each group) and (c) ENTPD5-overexpressing MIA PaCa-2 tumors (n = 15 each group). Shown is GLuc blood activity in relative light units (RLU) as a surrogate marker of the total tumor burden. d Liver metastasis is shown as FLuc activity (RLU, relative light units) of liver lysates. The number of animals with and without liver metastases in each group is indicated below the graph. e Pancreatic mouse tumors were analyzed by HE staining and immunohistochemistry for (mutant) p53, ENTPD5, and ITGA5. All boxplots show the minimum value, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum value. Single data points represent individual mice. Statistical significance was tested using two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test