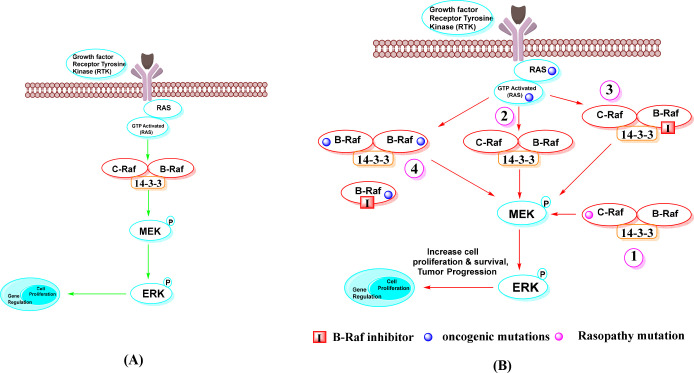
Figure 4.
Dimerization of Raf in cell signaling. Note: (A) In the normal RAS-dependent signaling pathway, Raf dimerization is required for Raf kinase activation and signaling to MEK for further cell proliferation and regulation. (B) In oncogenic states, it is required for MEK/ERK signaling, which is upregulated by Raf dimerization. These include: (1) mutant c-Raf protein with b-Raf in dimerization impaired kinase activity from normal to oncogenic, (2) RTKs and RasGTPases induced by mutation, (3) in the context of active Ras, treatment with ATP-competitive Raf inhibitors, and (4) Raf inhibitor resistance is mediated by self-homodimerizing BRAFV600E splice variants.