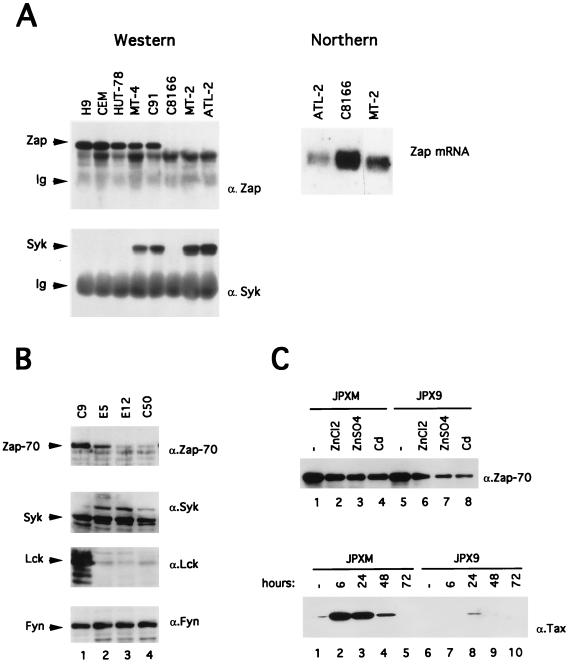
FIG. 5.
(A) Expression of Zap-70 and Syk in HTLV-1-infected T cells. For the Western blotting experiment (left part), cells (5 × 106) were lysed as described in Materials and Methods, and Zap-70 and Syk proteins were immunoprecipitated from 1 mg of cellular proteins with rabbit anti-Zap-70 or anti-Syk antisera. Zap-70 and Syk polypeptides were subsequently detected by using anti-Zap-70 or anti-Syk immunoblotting. The positions of the Zap, Syk, and immunoglobulins (Ig) are shown on the left. For the Northern blotting analysis (right part), 10 μg of total RNA from ATL-2, C8166, or MT-2 were electrophoresed, blotted, and hybridized with a 32P-labeled zap probe. (B) Western blot analysis of Zap-70 (α.Zap-70), Syk (α.Syk), Lck (α.Lck), and Fyn (α.Fyn) in Jurkat C9 cells, Tax- and Rex-positive cells (E5 and E12), and Tax-positive cells (C50). A total of 50 μg of protein was loaded into each lane. (C) In the top panel, a Western blot analysis of Zap-70 in JPXM and JPX9 cells treated 24 h with medium alone (lanes 1 and 5) or with heavy metals (lanes 2 to 4 and lanes 6 to 8) is shown. In the bottom panel, JPXM and JPX9 were cultured in medium alone (lanes 1 and 6) or in medium containing 30 μM CdCl2 (lanes 2 to 5 and lanes 7 to 10) for 6, 24, 48, or 72 h as indicated. Then, 50 μg of the extract was assayed to determine wild-type or mutated Tax expression by Western blotting.