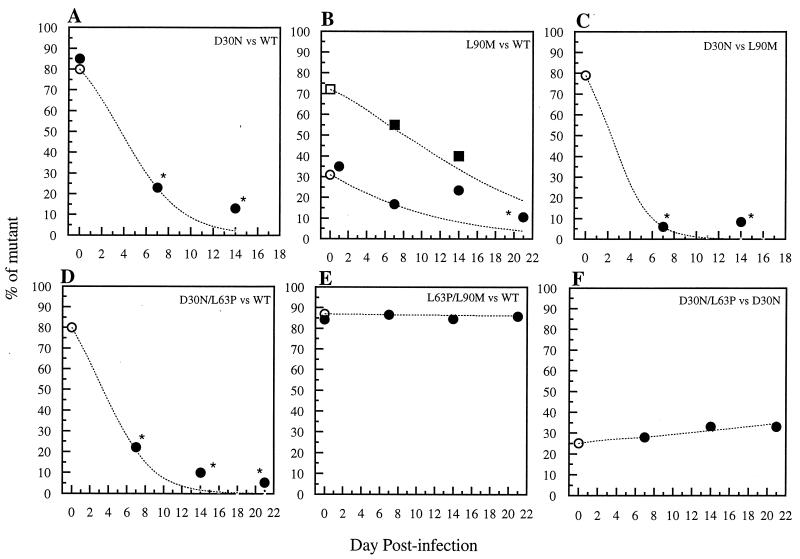
FIG. 2.
Fitness dynamics based on clonal analysis of mixed competitive infections of MT2 cells with drug-resistant HIV-1 mutants selected by nelfinavir or saquinavir in vivo. Coinfections were carried out with nonequivalent amounts of PI-resistant mutants versus either WT (NL4-3) or another mutant. The proportion of mutant virus, or the first mutant virus listed in the inset caption for each panel, is plotted over time. Two experiments, each initiated with a different proportion of the two viruses, are plotted in panel B; one experiment is plotted in each of the other panels. A mean of 15 clones was analyzed at each time point. (A) D30N versus WT starting with 85% D30N mutant, depicting the percentage of D30N mutant over time; (B) L90M versus WT starting with either 31% (circles) or 72% (squares) L90M mutant, depicting the percentage of L90M mutant over time; (C) D30N versus L90M starting with 80% D30N mutant, depicting the percentage of D30N mutant over time; (D) D30N/L63P versus WT starting with 80% D30N/L63P mutant, depicting the percentage of D30N/L63P mutant over time; (E) L63P/L90M versus WT starting with 87% L63P/L90M mutant, depicting the percentage of L63P/L90M mutant over time; (F) D30N/L63P versus D30N starting with 25% D30N/L63P mutant, depicting the percentage of D30N/L63P over time. Open symbols on day 0 refer to input TCID50 proportions (mutant TCID50/total TCID50). Solid symbols on day 0 refer to proportions of clones determined by clonal genotyping (number of mutant clones/total number of clones). The dotted lines show the percentage of each mutant predicted by a formula that modeled the effects of selection at a single locus in an asexual haploid population during continuous replication in overlapping generations (42) and which has been used in other studies of relative fitness of drug-resistant HIV-1 mutants (16, 22, 57); the relative fitness determined at day 7 was used to solve for proportions at other time points. The time points after day 7 do not agree perfectly with the model’s predictions in cases where the variants differ markedly, suggesting this model is inadequate. The asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference from day 0 (P < 0.05; Fisher’s exact test).