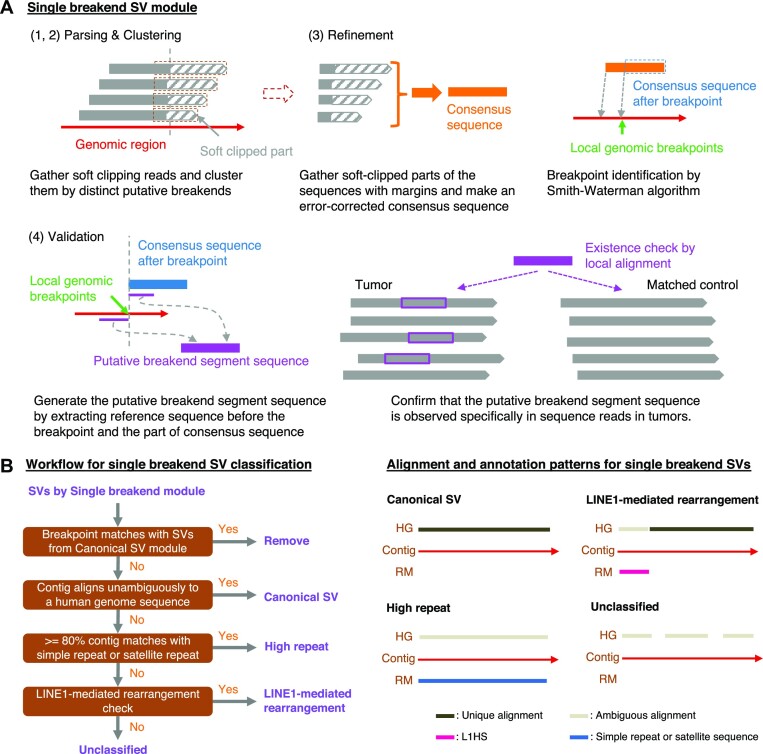
Figure 2.
Workflow of somatic SV detection and classification in nanomonsv single breakend SV module. (A) Single breakend SV module for nanomonsv consists of the following four steps. Parsing: the reads putatively supporting single breakend SVs are extracted from both tumor and matched control BAM files using soft clipping information in the CIGAR strings. Clustering: the reads from the tumor sample that presumably support the same single breakend SVs are clustered. The candidates are removed if apparent supporting reads are detected in the matched control sample (or non-matched control panel samples when they are available). Refinement: Gather the soft-clipped part of the reads with 100 bp margins inside the breakpoints and generate an error-corrected consensus sequence by two round iterations of all-vs-all alignment by minimap2 (29) and polishing with racon (78). Then, aligning the consensus sequence to those around the possible breakpoint regions by Smith-Waterman algorithm, we detect single base resolution breakpoints and the consensus sequence after the breakpoint. Validation: from the breakpoint determined in the previous step and the error-corrected consensus sequence after the breakpoint, we generate the ‘putative SV segment sequence.’ Then, as with Canonical SV module, the reads around the breakpoint of putative single breakend SVs are classified into ‘variant supporting read’ or ‘reference read’ for both tumor and matched control. Finally, candidate SVs with ≥3 variants supporting reads in the tumor and no variant supporting reads in the matched control sample are kept as the final single breakend SVs. See Supplementary Text for detail. (B) The left panel shows the chart for classifying SVs identified by Single breakend module. After removing SVs that share a breakpoint with SVs already detected via Canonical SV module, SVs are basically classified by integrating the alignment of contig sequences to the human reference genome (HG) and the annotation results by RepeatMasker (RM). The right panel shows the typical pattern of an alignment to HG and an annotation result by RM of the contig for each category. L1HS stands for the human LINE-1 (L1) element L1 Homo sapiens (L1Hs).