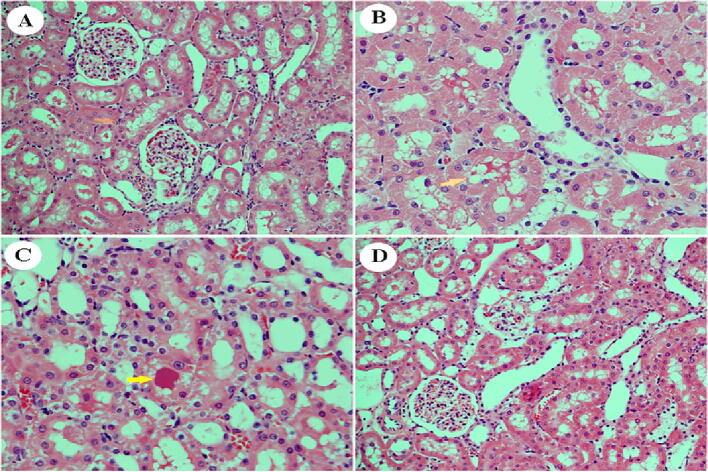
Fig. 9.
Effect of D. viscosa extract (150 mg/kg and 300 mg/kg) on STZ-induced pathological changes in the kidney as visualized with H&E staining, 400X. Section from the renal cortex of the control group shows the normal architecture of the proximal convoluted tubules (PT), distal convoluted tubules (DT), Bowman's capsule, and glomerulus (G) (A). Kidneys of untreated diabetic rats showed renal injury in the form of extreme vacuolation in the renal tubular cells (arrowhead) and the loss of nuclei because of karyolysis (B). The renal cortex of diabetic animals co-treated with D. viscosa (150 mg/kg) showed partial protection. Note the absence of tubular necrosis but with some residual hyaline casts (arrowhead) (C). Kidneys of diabetic animals co-treated with D. viscosa (300 mg/kg showed that the adverse effects of STZ on kidneys in the glomeruli and renal tubules were amended (D).