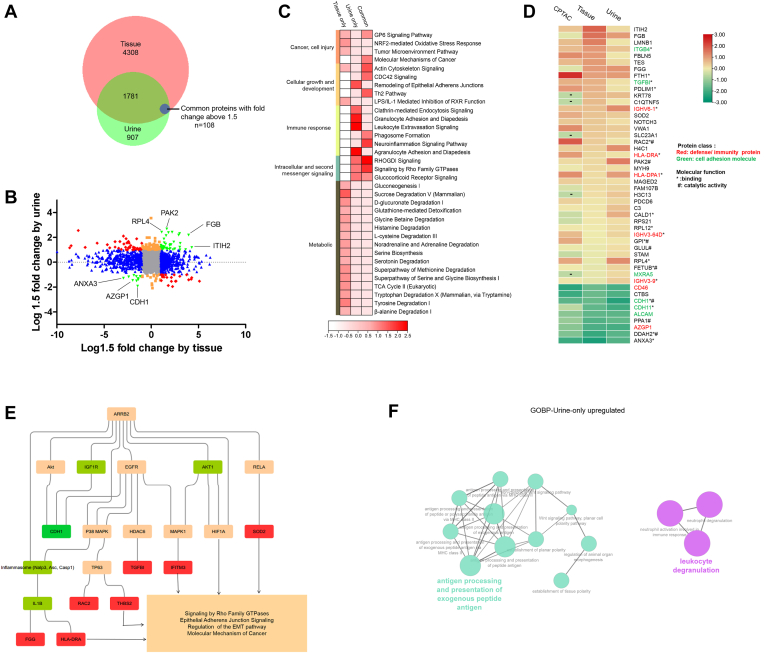
Fig. 3.
Integration of urine and tissue proteomes discovers consistent changes of cell adhesion molecular and immunity proteins in early-stage ccRCC.A, Venn diagram of identified proteins in tissue and urine datasets. Common differential proteins: Proteins with fold change above 1.5 (RCC vs. Control) in both tissue and urine. B, the distribution of the relative dominance of no change (gray), agree (green), tissue-only (blue), urine-only (orange), and disagree (red) proteins. Proteins were defined based on the consistency or inconsistency between the tissue and urine datasets. Agree proteins were those with the same direction of change in both tissue and urine datasets. No change proteins, in both tissue and urine, were not changed (within 1.5 fold change) between ccRCC and control. Tissue-only proteins varied between ccRCC and control in tissue dataset (larger than 1.5 fold), but not in urine (within 1.5 fold). Urine-only proteins varied in urine (larger than 1.5 fold), but not in tissue (within 1.5 fold). Disagree genes performed opposite direction of change in tissue and urine. C, pathway enrichment of tissue-urine agree proteins, tissue-only proteins, and urine-only proteins. D, proteins varied constantly in CPTAC tissue dataset, present tissue dataset, and urine dataset. Cell adhesion molecular and defense proteins account for the most (marked in green and red). E, casual network analysis predicted ARRB2 as the upregulator of downstream molecular and pathway disturbance. Molecular in red boxes: upregulated proteins in present study. Molecular in green boxes: downregulated proteins in present study; molecular in orange boxes: predicted to be activated status; molecular in grass green boxes: predicted to be inhibited status. F, GOBP (Go ontology for biological process) terms for urine-only upregulated proteins. ccRCC, clear cell renal cell carcinoma; CPTAC, Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium.