Figure 4: Non-lethal outcomes for apoptosis flatliners.
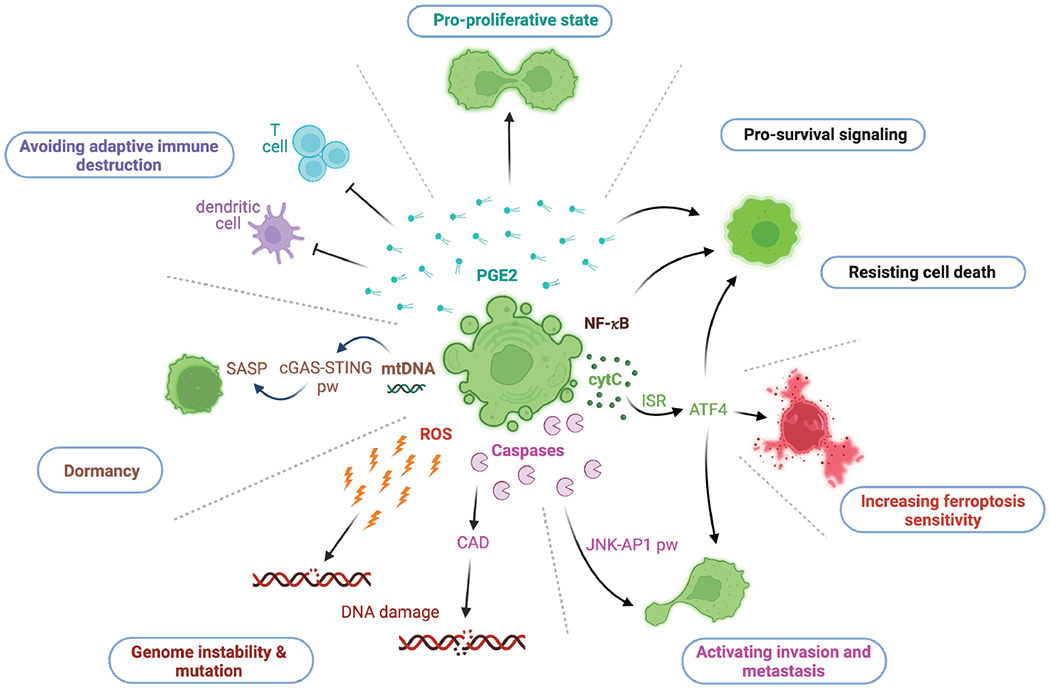
Illustration of evident consequences of the sublethal engagement of the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis and their main molecular players. The release of PGE2 relays inhibitory effects on T cells and dendritic cells. PGE2 can promote a pro-proliferative state and cell survival. NF-κB engages pro-survival signaling. Sublethal cytochrome c release can activate the ISR and thereby ATF4 translation. ATF4 impacts on various signaling pathways that lead to an escape from cell death, an increased sensitivity towards ferroptosis and a metastatic phenotype. Latter can also be promoted by sublethal caspase activation followed by subsequent initiation of the JNK-AP1 pathway. ROS and CAD can cause DNA damage, leading to genome instability and mutation. The cytosolic release of mtDNA can activate the cGAS-STING pathway, which promotes senescence and a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP).
