Figure 5. JSD26 treatment protects against acute kidney injury in mice.
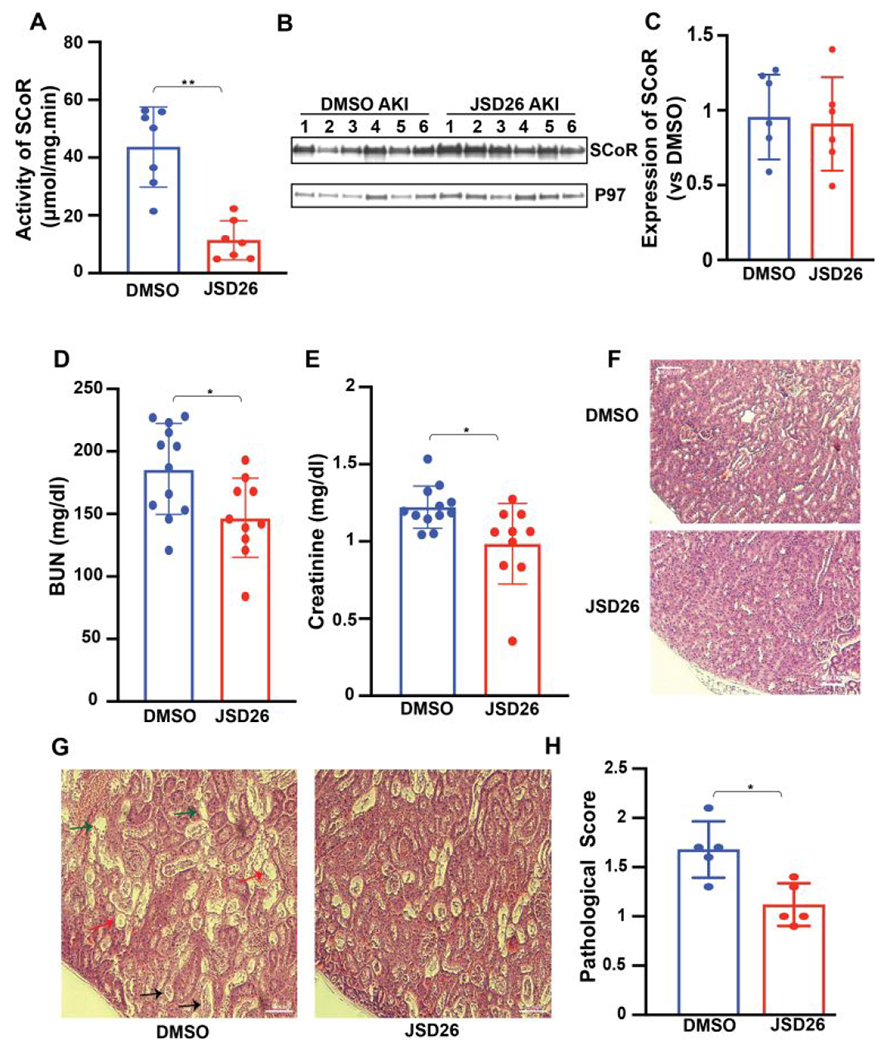
(A) SNO-CoA-metabolizing activity in kidneys from JSD26-treated mice (120 mg/kg i.p. 18h before surgery) assayed 24 hours post AKI (n=7). (B-C) Expression of SCoR2 in kidneys from JSD26-treated mice 24 hours post AKI (B) with quantification (C) (n=6). (D-E) Serum creatinine and BUN in JSD26-treated mice 24h after I/R-induced AKI (n≥10). (F) H&E stain in sham-surgery, and injury surgery vehicle- vs JSD26-treated kidneys. (G) H&E stain in injured kidneys, treated with vehicle or JSD26. AKI induced renal tubular injury includes severe tubular lysis (black arrow), loss of brush borders (green arrow) and sloughed debris in the tubular lumen (red arrow). (H) Pathological scores of tubular injury in vehicle-treated or JSD26-treated mice (n=5 mice per group). All results are presented as mean ± SD. Two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to detect significance. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01.
