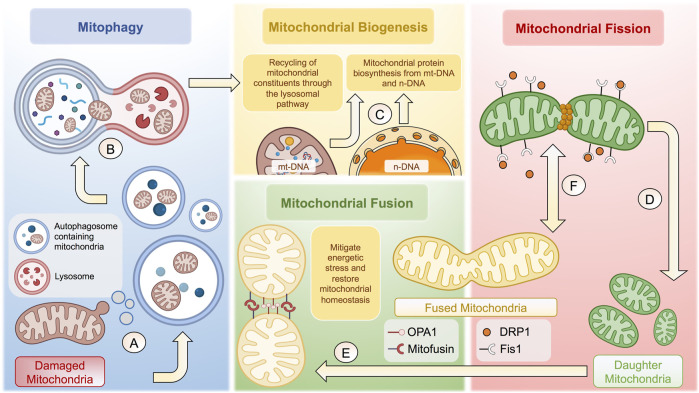
FIGURE 1.
Cellular and molecular mechanisms behind mitochondrial homeostasis. (A) Damaged membrane microdomains of mitochondria are packaged in autophagosomes to follow the lysosomal pathway. (B) Autophagosomes containing mitochondria fuse with lysosomes to form autophagolysosomes to degrade mitochondria. (C) Once degraded, mitochondrial constituents are recycled to potentiate mitochondrial biogenesis together with proteins synthetized from n-DNA and/or mt-DNA. (D) Mitochondrial fission is tightly regulated through Fis1-dependent recruitment of DRP1, which generates a constriction ring to give rise to two daughter mitochondria. (E) Resulting mitochondria can undergo mitochondrial fusion to increase the mitochondrial biomass and thus mitigate energetic stress through OPA1 and Mitofusin proteins. (F) The balance between mitochondrial fusion and fission is highly dynamic, depending of various factors, including the bioenergetic status and cell-specific functions, among many others. The complexity of the regulation of mitochondrial homeostasis is not fully depicted. The figure was created in BioRender.com.