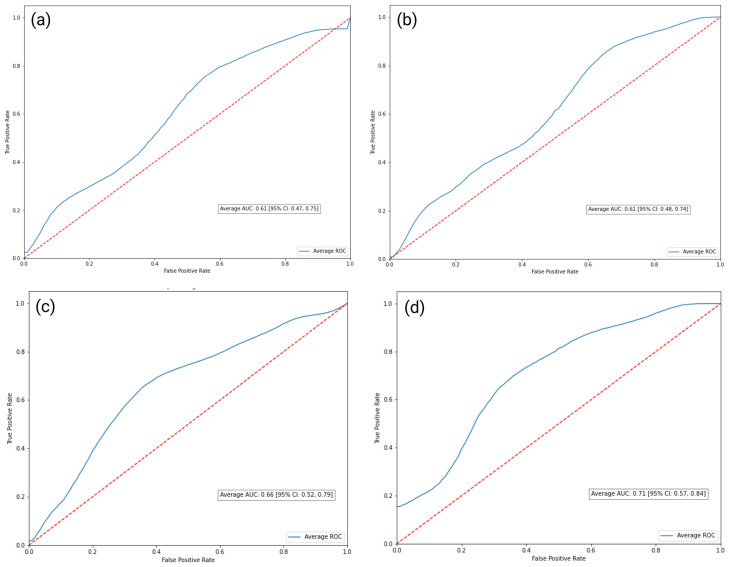
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the classification methods employed for the differentiation of inflammatory BME. Initially, simple linear models like Logistic Regression (a) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) (b) were selected, followed by Random Forest (RF) architecture (c), and, finally, culminating in the application of a gradient boosting method using the robust XGBoost algorithm (d). Each model’s performance was optimized by tuning its hyperparameters through a Random Search approach, which maintains high-quality results while conserving computational resources. The figure illustrates the relative performance of each method (SVM, Logistic Regression, RF, and XGBoost) using, as a performance metric, the Area Under the Receiver-Operating Characteristic curve (AUC-ROC), demonstrating the superior performance of the XGBoost model with an AUC-ROC of 0.71. (Created with BioRender [11], 18 June 2023).