Figure 1.
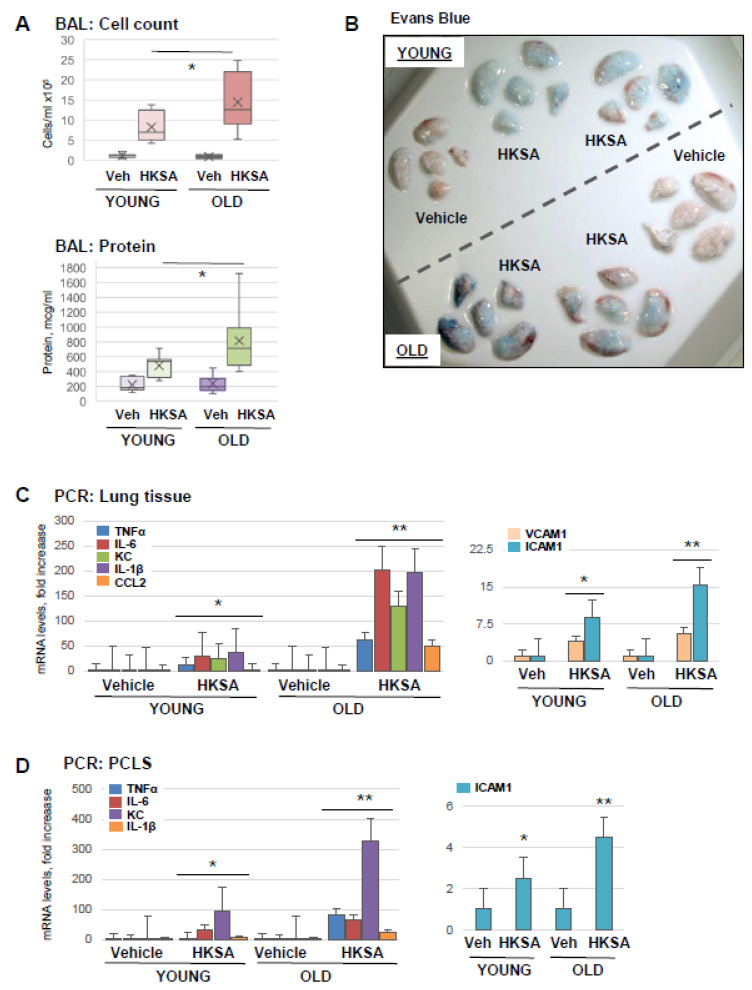
Old mice are more susceptible to HKSA-induced lung injury and inflammation. Young (aged 2–4 months) and old (aged 18–24 months) mice were exposed to HKSA (intranasal, 4 × 108 bacterial particles) for 24 h. (A) BAL was collected from both groups, and total cell counts and protein content were determined; n = 6, * p < 0.05. (B) Evans blue dye was injected (i.v., 30 mg/kg) into mice 2 h before termination of the experiment, and excised lungs were visualized for the accumulation of the dye in lung parenchyma. Shown are representative images of six independent experiments. (C) Transcriptional activation of proinflammatory marker genes was measured by qRT-PCR analysis of total RNA extracted from lung tissue. Data shown as fold increase over control; n = 3, * p < 0.05 vs. Vehicle, ** p < 0.05 vs. young group. (D) PCLS were cultured as described in Methods and subjected to HKSA challenge (108 cells/mL, 6 h). mRNA expression of indicated genes was determined via qRT-PCR n = 3, * p < 0.05 vs. Vehicle, ** p < 0.05 vs. young group.